Figure 3. AR influenced HDAC7-NCoR association.
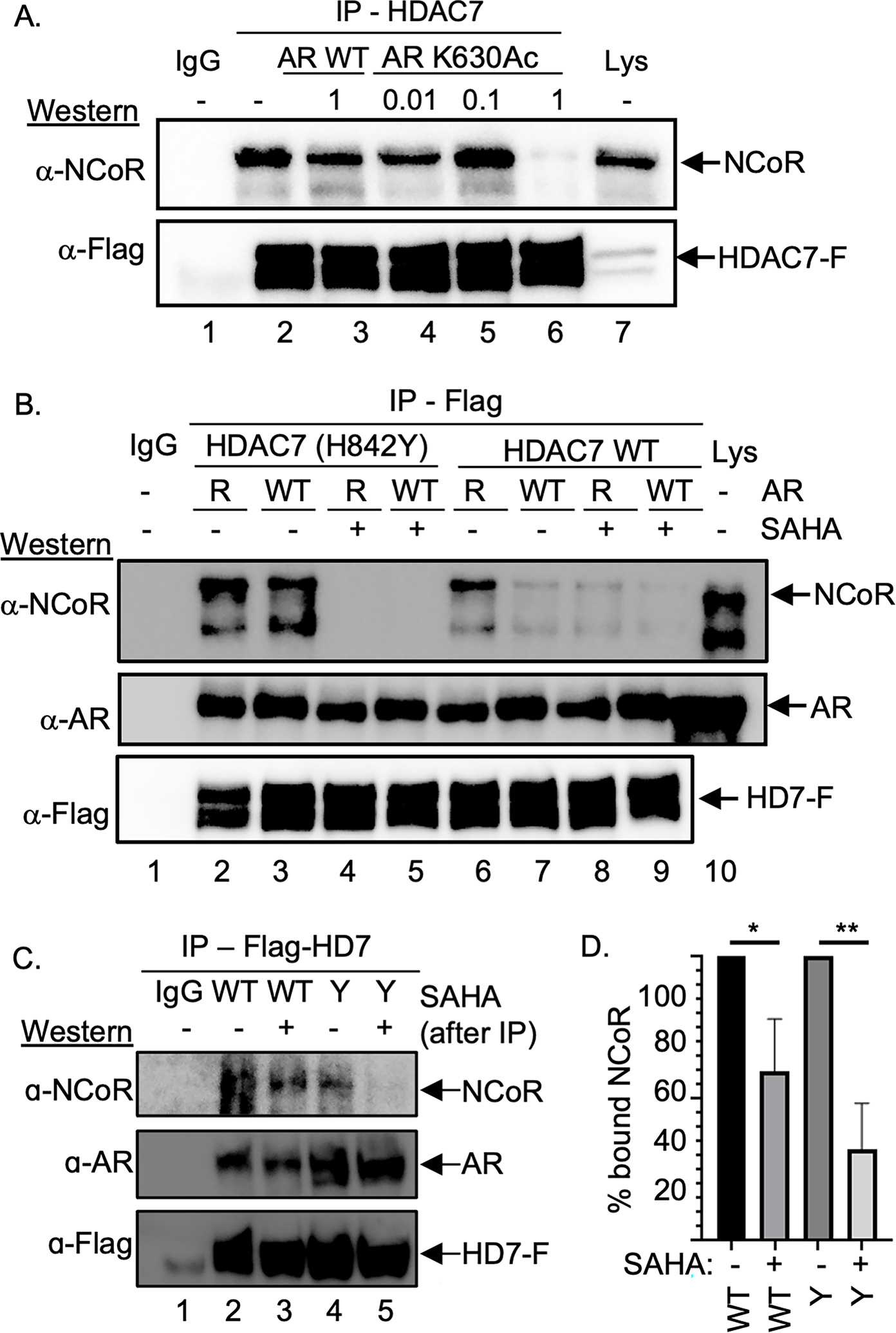
(A) Flag-tagged HDAC7 was expressed in HEK293 cells, which were then treated with SAHA (10 μM) to induce acetylation, followed by lysis, immunoprecipitation (IP) in the presence of different mM concentrations of AR K630Ac or AR WT peptide, SDS-PAGE separation, and western blot analysis with NCoR and Flag (HD7-F) antibodies. Repetitive independent trials are shown in Figure S5A. (B) HDAC7 wild type (WT) or GOF mutant were co-expressed with AR WT or K630R mutant in HEK293 cells, followed by lysis, immunoprecipitation (IP) of HDAC-Flag from the lysates, SDS-PAGE separation, and western blot analysis with NCoR, AR, or Flag (HD7-F) antibodies. As a gel migration control, lysate (Lys) from transfected cells were included. Repetitive independent trials are shown in Figure S5B. (C) HDAC7 wild type (WT) or GOF mutant (Y) were co-expressed with AR WT in HEK293 cells, which were then treated with SAHA (10 μM) to induce acetylation. After lysis and immunoprecipitation (IP), bound proteins were washed with a high salt (500 mM) buffer, before SAHA (100 μM) or DMSO vehicle was added and further washed. Bound proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized with NCoR, AR, or Flag (HD7-F) antibodies. Repetitive independent trials are shown in Figures S5C. (D) NCoR proteins levels from three independent trials from part C and Figures S5C were quantified, normalized to samples without SAHA (set to 100%), and plotted with mean and standard error shown (Figure S5D). * = p<0.05, ** = p < 0.01. All trials include a bead binding control using lysates without expression of HDAC7-Flag (IgG).
