Figure 7. Proposed model of class IIa HDAC “reader” function.
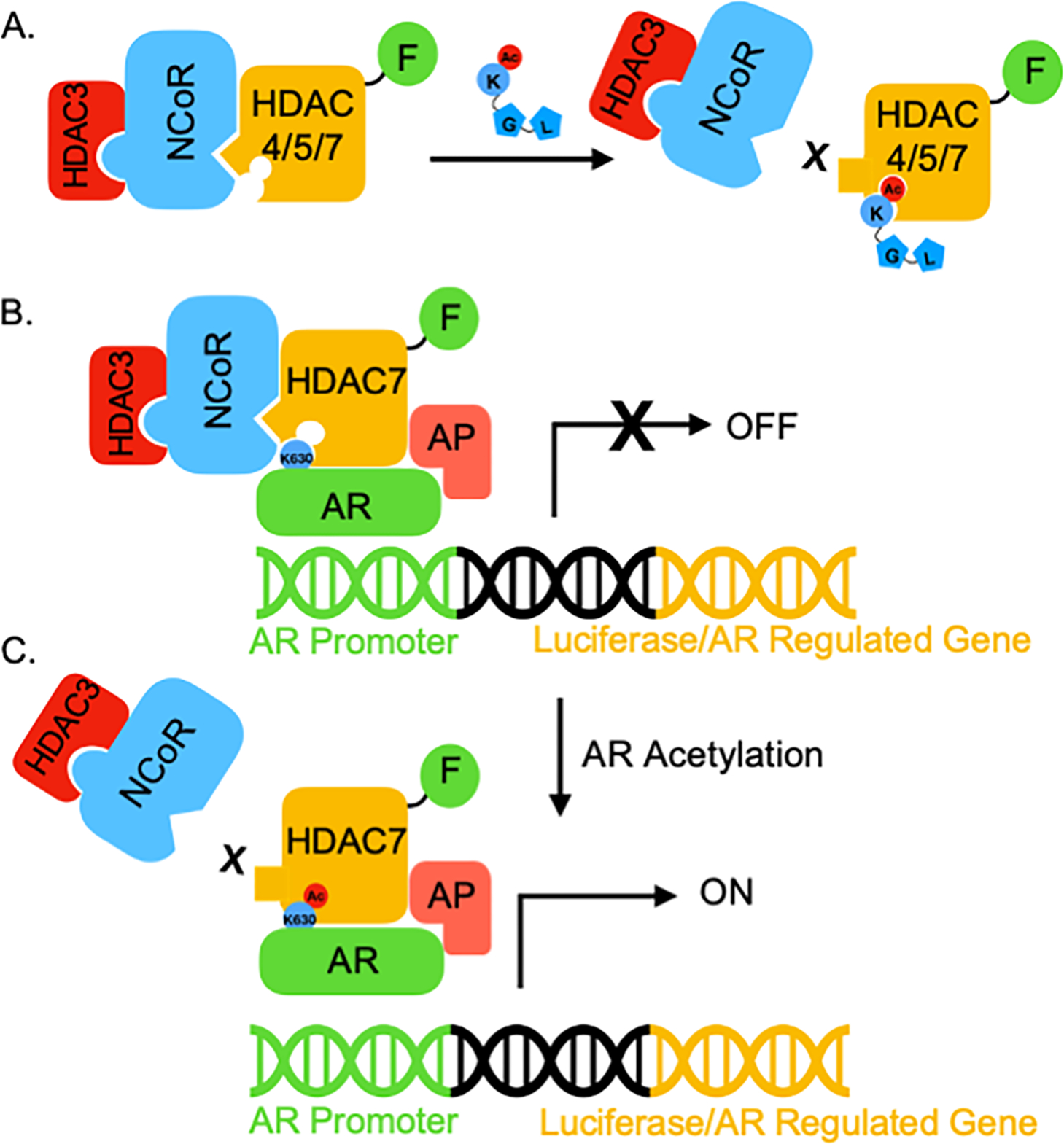
(A) HDAC4, 5, and 7 can act as epigenetic ‘readers’ that recruit the NCoR-HDAC3 complex, which is disrupted when acetyllysine binds to the inactive active site. (B) HDAC7 bridges unacetylated AR and NCoR to repress the activity of AR through HDAC3 recruitment. This acetylation-independent binding of AR to the HDAC7-NCoR-HDAC3 complex might be direct or indirect through associated proteins (AP), and is likely mediated outside of the HDAC7 active site. (C) Once AR is acetylated on its critical lysine K630, acetyl-K630 binds the HDAC7 active site to dissociate the NCoR-HDAC3 complex. Without epigenetic repression by HDAC3, AR-mediated transcription is active.
