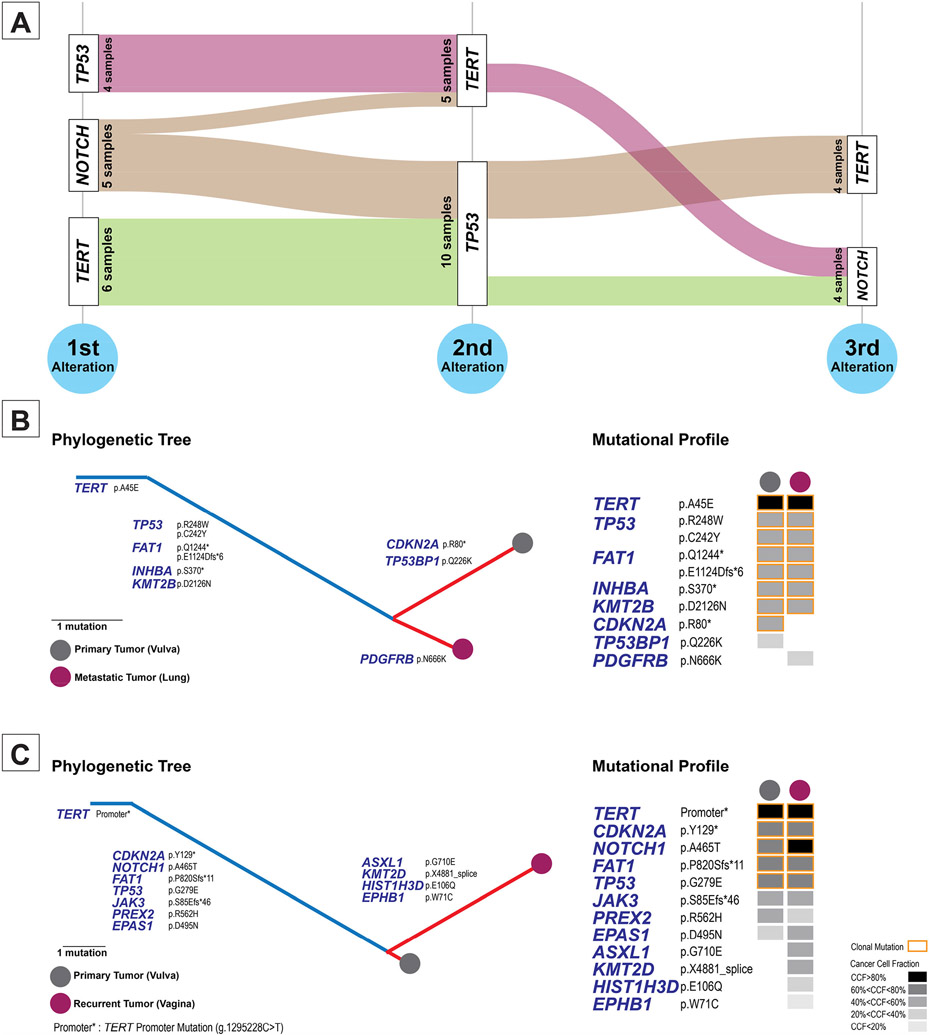
Figure 4 – Clonal evolution of HPV-independent vulvovaginal squamous cell carcinomas.
(A) Alluvial graph showing the distribution of the three genomic alterations in vulvovaginal squamous cell carcinomas with the highest cancer cell fractions. All HPV-independent vulvovaginal squamous cell carcinomas have truncal alterations in a combination of TP53, TERT and NOTCH1 genes and any of these genes can have the highest cancer cell fraction in the tumors. (B-C) Phylogenetic reconstruction of the tumor evolution in two cases of metastatic/recurrent vulvovaginal squamous cell carcinomas.