Figure 2.
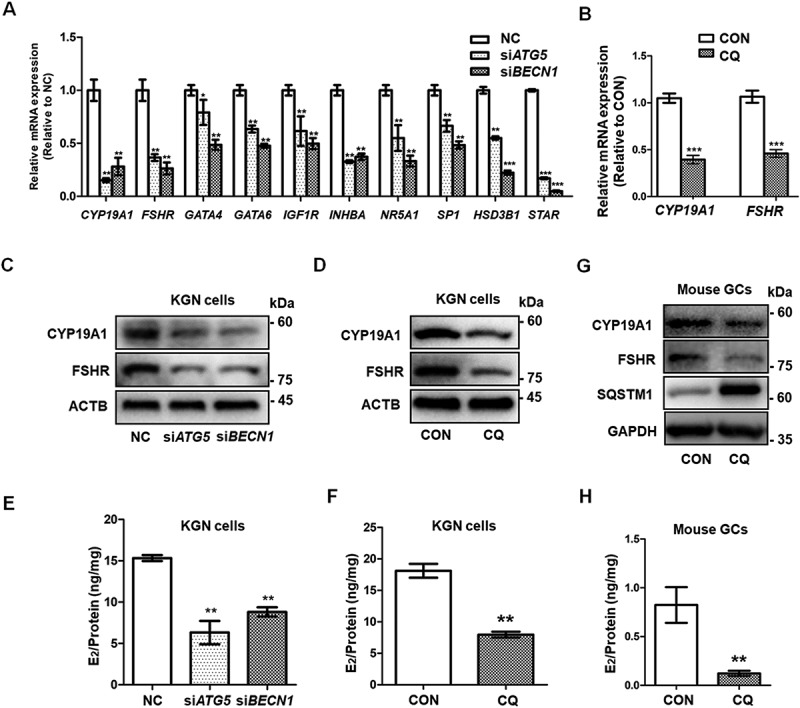
Autophagy inhibition leads to insufficient differentiation of GCs. (A) After siRNA transfection of KGN cells for 48 h, the mRNA expression of the genes related to GC differentiation and steroidogenesis, including CYP19A1, FSHR, GATA4, GATA6, INHBA, SF1, SP1, HSD3B1, and STAR, showed significant downregulation in both the siATG5 and siBECN1 groups. GAPDH served as the internal control. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. vs. NC. (B) After treatment of KGN cells with CQ, the mRNA expression of CYP19A1 and FSHR was downregulated compared to controls. GAPDH served as the internal control. Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3. ** P < 0.01 vs. CON. (C and D) Protein levels of CYP19A1 and FSHR were decreased in KGNs transfected with siATG5 and siBECN1 or pretreated with CQ as measured by Western blot. ACTB was used as the loading control. (E) E2 production in KGN cell supernatant was decreased in both the siATG5 (6.32 ± 1.41 ng/mg) and siBECN1 (8.81 ± 0.56 ng/mg) groups compared to the NC group (15.33 ± 0.36 ng/mg). Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01 vs. NC. (F) E2 production in CQ-treated KGN cells (7.96 ± 0.47 ng/mg) was lower than that in the control group (18.11 ± 1.10 ng/mg). Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01 vs. CON. (G) Mouse GCs were harvested and cultured in vitro. After 48 h treatment with 50 μM CQ, the protein levels of CYP19A1 and FSHR were lower than those in the control group. GAPDH was used as the loading control. (H) The E2 production was decreased in CQ-treated mouse GCs (0.12 ± 0.03 ng/mg) compared to the control group (0.82 ± 0.18 ng/mg). Data are presented as mean ± SD, n = 3, **P < 0.01 vs. CON.
