Figure 6.
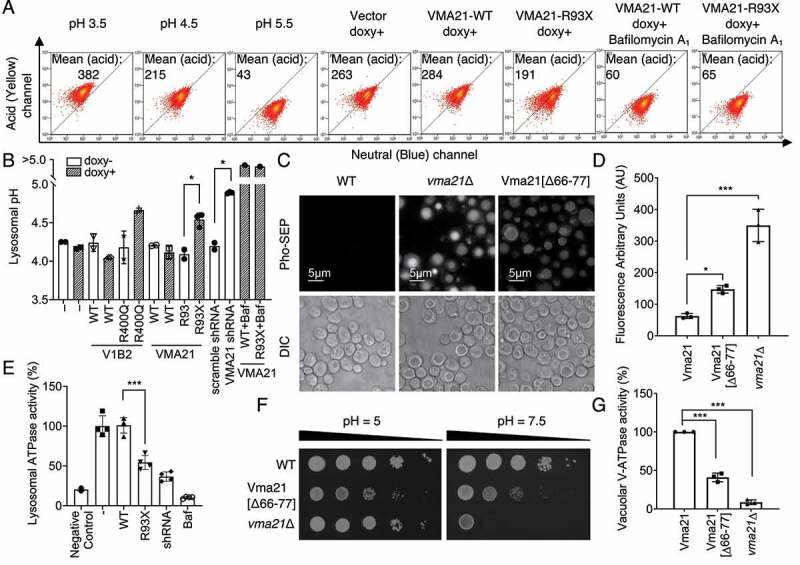
Follicular-lymphoma associated VMA21 mutations reduce the ability of the V-ATPase to acidify lysosomes because of reduced lysosomal V-ATPase activity. (A) Stable HEK293T cells carrying inducible WT or MUT VMA21 were induced with doxycycline and loaded with the pH indicator dextran-conjugated LysoSensor Blue/Yellow. Untransfected cells were treated with EMS buffer calibrated to pH 3.5, pH 4.5 or pH 5.5. The fluorescence intensity of cell suspensions was read using flow cytometry. The mean fluorescence intensity of the yellow dye signal is a measure of lysosomal pH. (B) Estimation of lysosomal pH from data generated as in panel A with n = 3. (C) Vacuolar pH was measured using a pH-sensitive Pho8-SEP protein that exhibits stronger fluorescence with higher pH. Upper images show the fluorescence signal of Pho8-SEP; lower images show the corresponding light microscopy. (D) The quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity of Pho8-SEP in WT, Vma21[∆66-77], and vma21∆ cells. Mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Unpaired, 2-tailed t-test with Bonferroni correction; *: p < 0.05, ***: p < 0.005. (E) Lysosomal V-ATPase activity (see Materials and Methods) in lysosomal preparations isolated via lyso-IP from cells carrying no lyso-IP bait (negative control), (-) empty vector, VMA21 WT, VMA21 93X, an shRNA targeting VMA21 or bafilomycin A1. n = 4, unpaired, 2-tailed t-test; ***: p < 0.005. (F) Growth of yeast strains (WT, Vma21[∆66-77], and vma21∆) on YPD plates buffered to pH 5.0 and on YPD plates buffered to pH 7.5. (G) The quantitative V-ATPase activity of WT, Vma21[∆66-77], and vma21∆ vacuoles were measured. After vacuole isolation, the release of inorganic phosphate arising from hydrolysis of ATP was determined. Mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Unpaired, 2-tailed t-test; ***: p < 0.005.
