Figure 3.
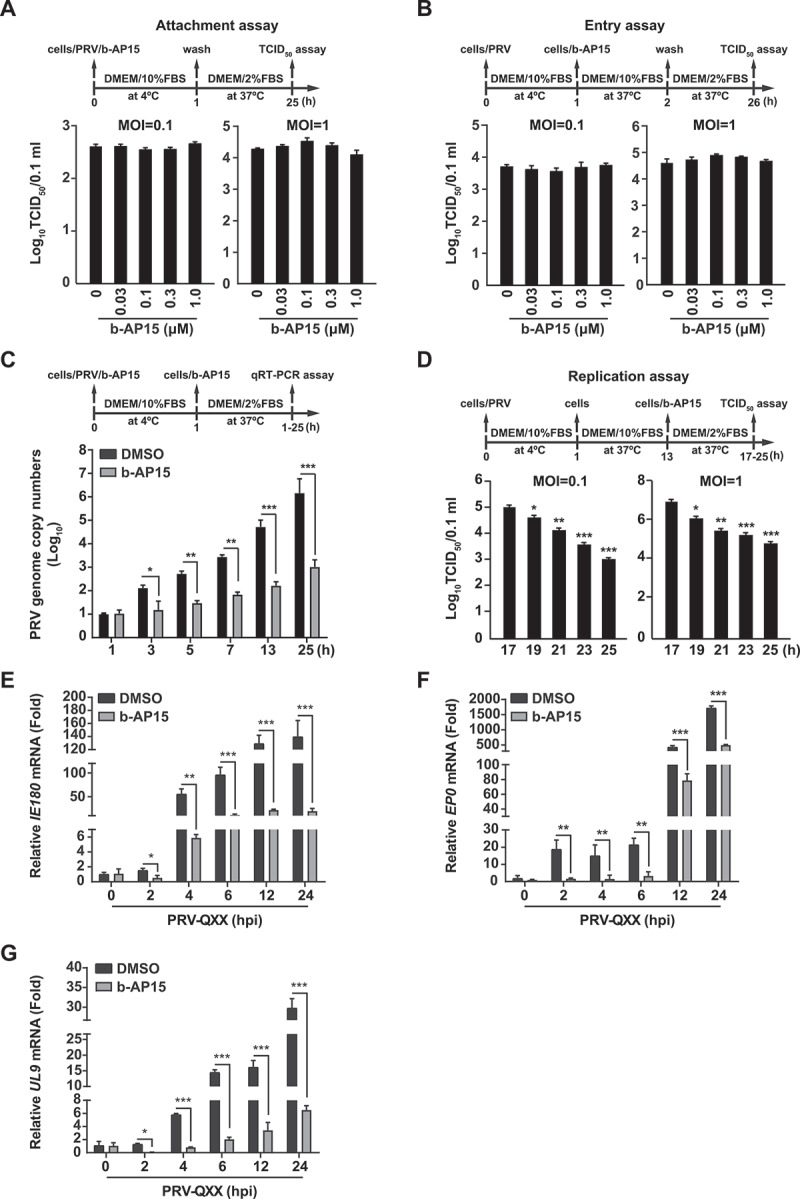
B-AP15 influences PRV replication. (A) PK-15 cells were incubated with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1 and 1) combined with b-AP15 (0–1 μM) for 1 h at 4°C. After washing with cold PBS 3 times, cells were cultured in DMEM with 2% FBS for 24 h at 37°C. An attachment assay was assessed using the TCID50 assay of viral titers. (B) PK-15 cells were incubated with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1 and 1) for 1 h at 4°C and then in DMEM with 10% FBS containing b-AP15 (0–1 μM) at 37°C. After 1 h to allow viral entry, cells were cultured in DMEM with 2% FBS for 24 h at 37°C. An entry assay was assessed using a TCID50 of viral titers. (C) PK-15 cells were incubated with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) combined with b-AP15 (1 μM) for 1 h at 4°C. After washing with cold PBS 3 times, cells were cultured in DMEM with 2% FBS combined with b-AP15 (1 μM) for 0–24 h at 37°C. PRV genome copy numbers were assessed by qRT-PCR analysis. (D) PK-15 cells were incubated with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1 and 1) at 4°C for 1 h and then in DMEM with 10% FBS at 37°C for 12 h. Cells were then cultured in DMEM with 2% FBS containing b-AP15 (1 μM) for 4–12 h at 37°C. A replication assay was assessed using the TCID50 assay of viral titers. (E–G) PK-15 cells were infected with PRV-QXX (MOI = 0.1) and simultaneously treated with DMSO or b-AP15 (1 μM) for 0–24 h. The mRNA levels of PRV IE180 (E), EP0 (F) and UL9 (G) were assessed by qRT-PCR analysis. hpi, hour post infection. Data were shown as mean ± SD based on three independent experiments. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test.
