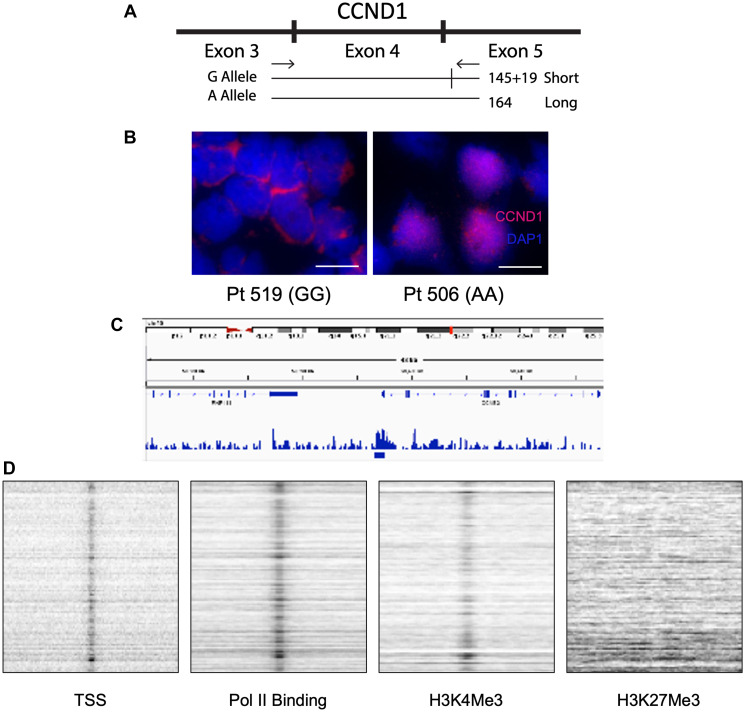
Figure 6. The G/A870 CCND1 polymorphism correlates with cyclin D1 cellular localization and differentiates blastic vs. non-blastic MCL.
(A) Schematic of CCND1 exons 3,4 and 5 and the splice site with the G allele that is not present with the A allele. (B) Immunohistochemistry staining of homozygous GG (Left) vs. homozygous AA (Right) MCL patient for cyclin D1 and DAPI. Scale bars are 10 μM. (C) Representative enrichment profile snapshot of genome browser from cyclin D1 ChIP-seq depicting sites of cyclin D1 binding to the genome. (D) Colocalization signals of cyclin D1 with transcription start sites (TSS), RNA polymerase II (Pol II), H3K4Me3 and lack of colocalization with H3K27Me3 from cyclin D1 ChIP-seq.