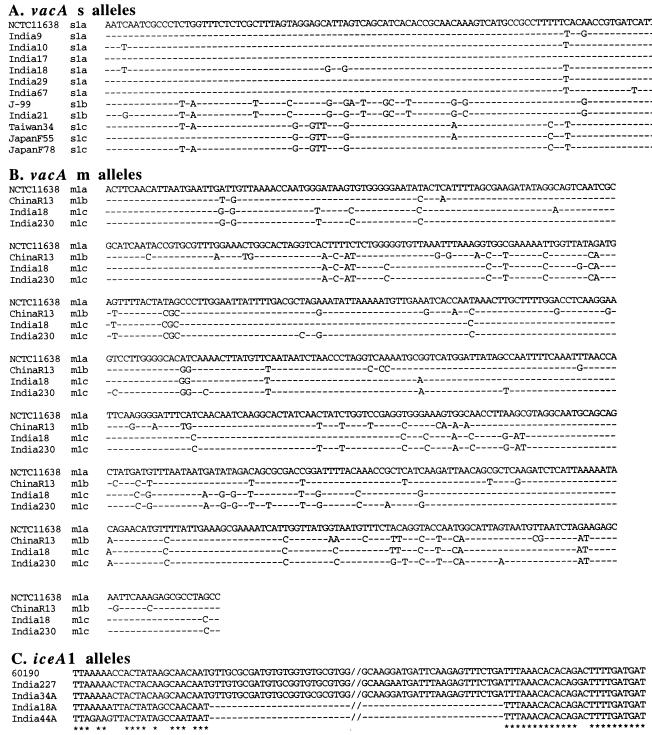
FIG. 4.
DNA sequence alignments, illustrating motifs found in H. pylori strains from Calcutta. Sequences from non-Indian strains that were used here were from public databases, as indicated. (A) vacAs region sequences, showing differences between vacAs1a, -s1b, and -s1c type alleles. vacAs1a alleles are common in the Calcutta H. pylori strains, whereas vacAs1c alleles are most common elsewhere in Asia. Each of the 97-bp sequences presented here starts at position 27 of a reference vacA open reading frame (GenBank accession no. U07145). Identical nucleotides are indicated by hyphens. GenBank accession numbers for the sequences depicted here are U07145 (NCTC11638), AF217728 (India9), AF217729 (India10), AF217730 (India17), AF217731 (India18), AF217734 (India29), AF217735 (India67), AE001511 (J99), AF217732 (India21), AF091830 (Taiwan34), AF049632 (Japan55), and AF049638 (Japan78). (B) vacAm1 middle region sequences, showing differences among vacAm1a, vacAm1b, and two of the representative vacAm1c allele types that we characterized. The vacAm1c alleles, which were common in Calcutta strains, were rare in populations from outside India that have been studied to date. Each of the 650-bp sequences presented here corresponds to nucleotides (nt) 2060 to 2709 of the vacA gene of reference strain NCTC11638 (Genbank accession no. U07145). GenBank accession numbers for the sequences depicted here are U07145 (NCTC11638), AF035610 (ChinaR13), AF220110 (India18; strain 5 in Fig. 3) and AF220117 (India230; strain 6 in Fig. 3). (C) Alignment of four iceA1 genes of Calcutta isolates, along with reference strain 60190 (GenBank accession no. U43917). The sequences presented here correspond to nt 426 to 558 in India227 (accession no. AF239991), nt 446 to 558 in India34A (accession no. AF239992), nt 430 to 478 in India18A (accession no. AF239993), and nt 423 to 471 in India44A (accession no. AF239994).