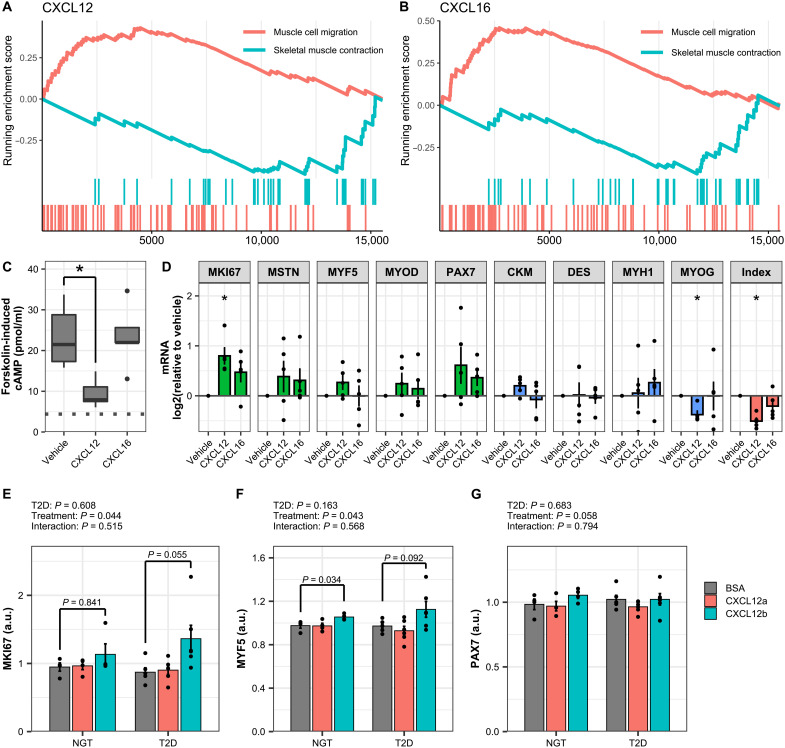
Fig. 6. CXCL12 alters skeletal muscle cell differentiation.
(A and B) Gene set enrichment analysis of genes correlated with CXCL12 and CXCL16 in the RNA sequencing of skeletal muscle biopsies. The pathway “muscle cell migration” was positively enriched, while “skeletal muscle contraction” was negatively enriched. (C) Inhibition of forskolin-induced cAMP production by CXCL12 or CXCL16 (100 ng/ml) measured in C2C12 myotubes as described in Materials and Methods. Box-and-whisper plots from five independent experiments. *P < 0.05. (D) C2C12 myoblasts were exposed to CXCL12 or CXCL16 (100 ng/ml) every other day for 5 days during the differentiation process as described in Materials and Methods. mRNA expression of genes markers of myoblasts or myotubes was measured by qPCR. Data are means ± SE, n = 5 independent experiments, repeated-measures ANOVA with Tukey’s posttest comparing cytokines to vehicle, *P < 0.05. (E to G) Primary human skeletal muscle cells from individuals with type 2 diabetes (T2D) or NGT were exposed to CXCL12a/SDF-1α or CXCL12b/SDF-1β (100 ng/ml) during the differentiation process as described in Materials and Methods. mRNA expression of gene markers of myoblasts or myotubes were measured by qPCR. Data are means ± SE, n = 4/6 cultures from independent donors (NGT/T2D).