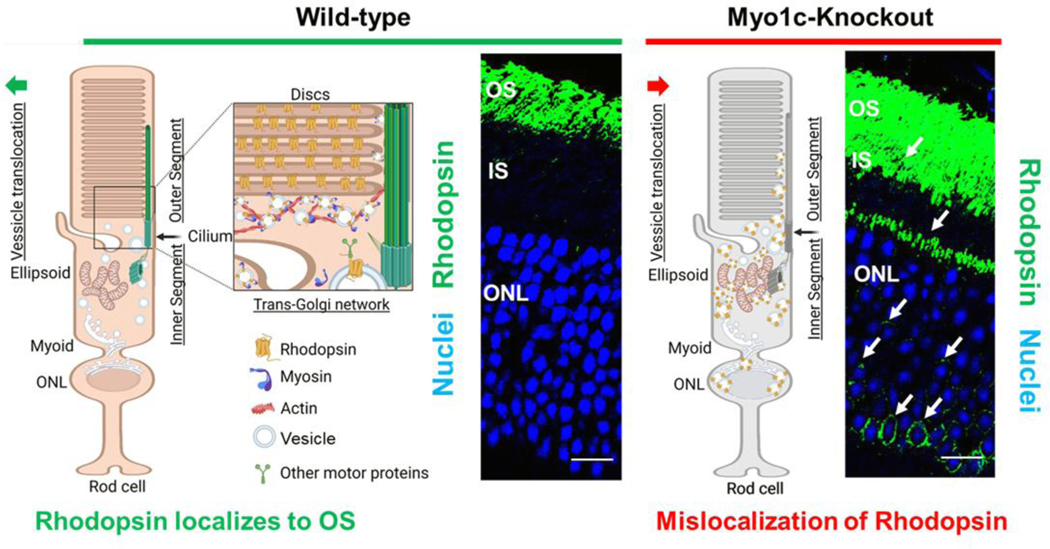
Figure 3: Proposed role for MYO1C in retinal cell physiology.
The impact of the unconventional motor protein MYO1C for Rhodopsin localization to photoreceptor outer segments (OS) was established recently (108). The model shows the effects of Myo1c deletion on the distribution of Rhodopsin in photoreceptor inner segments (IS) and outer nuclear layers (ONL). The model was created with BioRender.com. (A) MYO1C regulates the localization of Rhodopsin to the photoreceptor OS. The interaction between MYO1C and Rhodopsin mediates their translocation to photoreceptor compartments using actin as tracks. (B) The loss of MYO1C results in Rhodopsin mislocalization, leading to a retinal diseased phenotype like those observed in C’-terminal Rhodopsin mutants, in relevant mouse models.