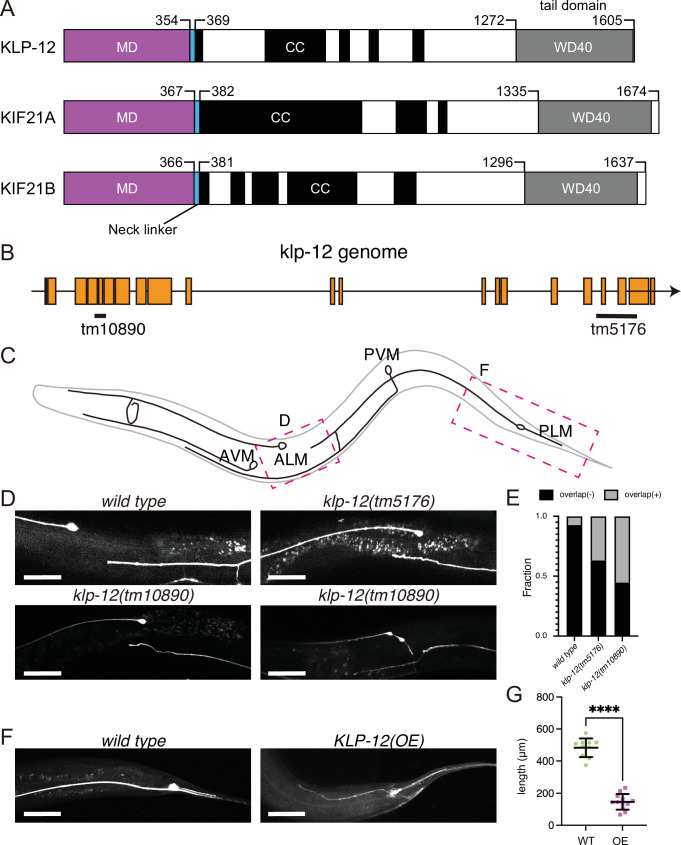
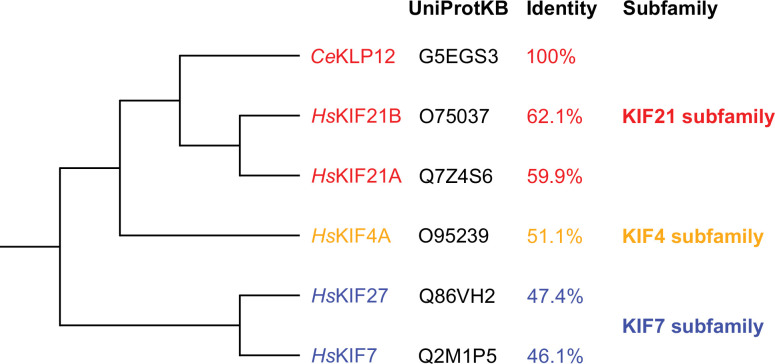
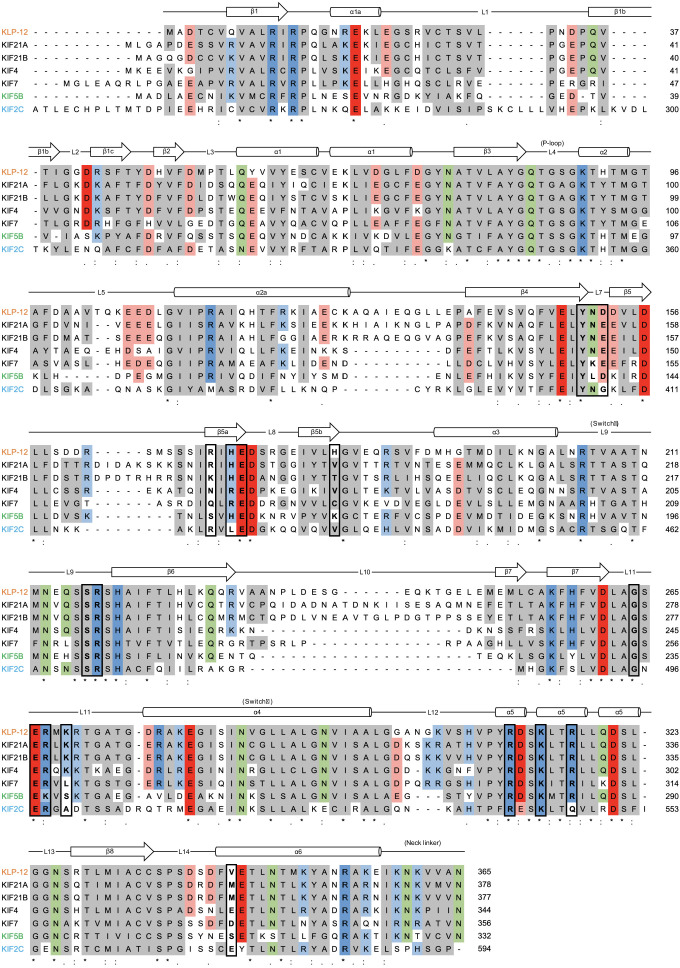
Figure 1. KLP-12 is an ortholog of KIF21A and KIF21B that regulates axonal length.
(A) Schematic presentation of the domain organization of the KIF21 subfamily: C. elegans KLP-12, human KIF21A, and KIF21B consist of a motor domain (MD; magenta), neck linker (blue), coiled-coil domains (CC; black), and WD40 domain (WD40; gray). Phylogenetic tree and sequence alignment of kinesin-4 family are available in Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Figure 1—figure supplement 2, respectively. (B) Schematic presentation of the genomic structure of C. elegans klp-12 and mutant alleles used in this study. tm10890 is a deletion mutant that induces frameshift, whereas tm5176 deletes WD repeats domain. (C) Schematic presentation of the mechanosensory neurons in C. elegans. Areas observed in panels (D) and (F) are shown by magenta boxes. ALM: anterior lateral mechanosensory, AVM: anterior ventral mechanosensory, PLM: posterior lateral mechanosensory, and PVM: posterior ventral mechanosensory neurons. (D and E) The tiling of ALM and PLM neurons. (D) Representative images of ALM and PLM neurons in wild type and klp-12 mutant worms. The axonal tip of PLM neurons does not overlap with the cell body of ALM neurons in wild type, while the axonal tip of PLM neuron overlaps with the ALM cell body in klp-12(tm5176) and klp-12(tm10890) mutant alleles. Bars, 50 µm. (E) The percentage of ALM and PLM overlap in wild-type, klp-12(tm5176), and klp-12(tm10890) mutant alleles in day 3 adult worms. n=55 in wild type, 60 in klp-12(tm5176), and 58 in klp-12(tm10890) worms. (F and G) Overexpression of KLP-12 suppresses the elongation of mechanosensory axon. (F) The morphology of wild type and klp-12-overexpressed PLM neurites. Bar, 50 µm. (G) The lengths of PLM neurites are plotted. Each dots show the length of axons in each worm. Bars represent mean ± standard deviation. n=10 in wild-type and 12 in KLP-12-expressing axons. ****, p<0.0001, Welch’s t test.