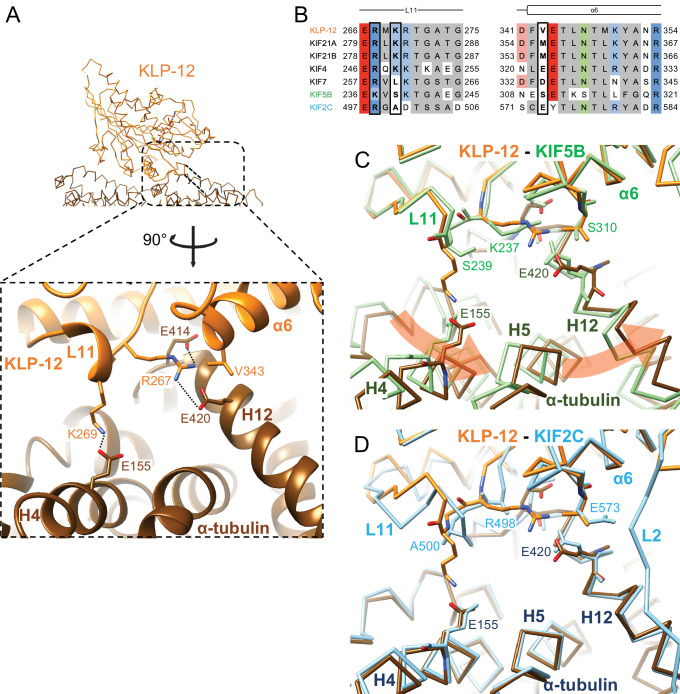
Figure 5. Microtubule binding interface of kinesin-4 KLP-12 at α-tubulin.
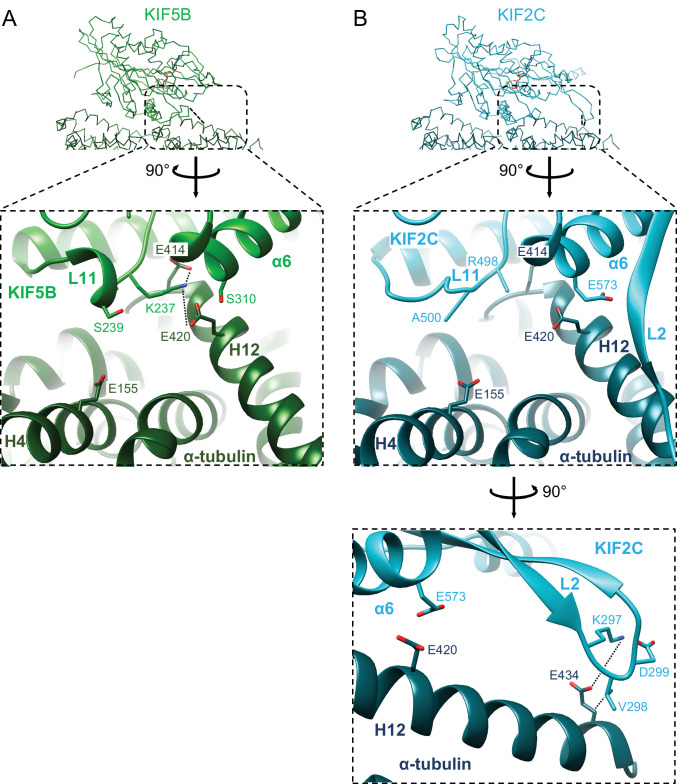
(A) KLP-12 Arg267 and Lys269 in loop L11 interact with α-tubulin Glu414 and Glu420 in helix H12 and Glu155 in helix H4, respectively. See Video 2 for detail. The interfaces of KIF5B and KIF2C at α-tubulin are available in Figure 4—figure supplement 1. (B) Sequence alignment of the kinesin-4, KIF5B, and KIF2C residues at the interacting area. Interacting residues are marked by squares. (C) Superimposition of Cα chain trace models of the KLP-12 complex (orange) and KIF5B complex (green) at kinesin. The rotation direction of α-tubulin between KLP-12 and KIF5B at helices H4, H5, and H12 is illustrated as a red arrow. (D) Superimposition of Cα chain trace models of the KLP-12 complex (orange) and KIF2C complex (cyan) at kinesin.