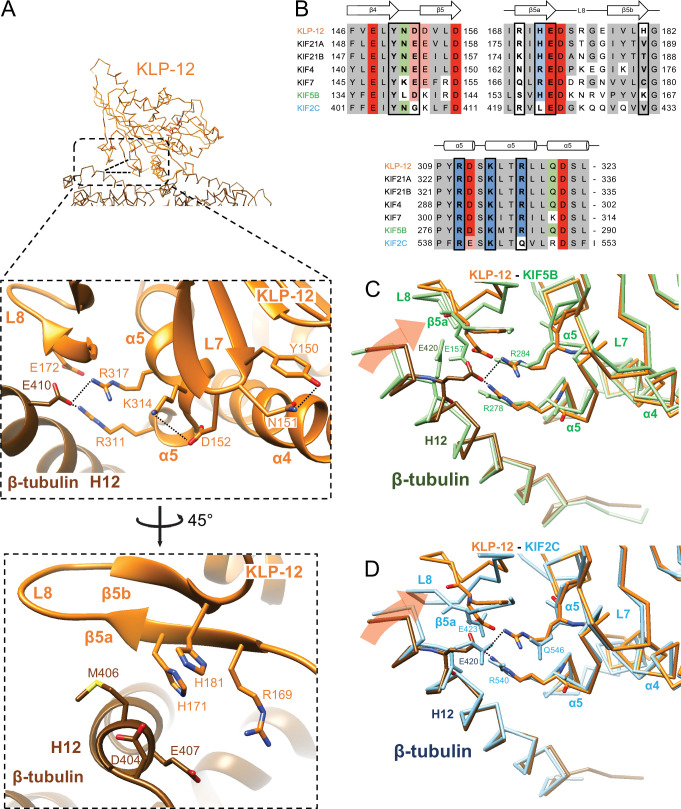
Figure 6. Microtubule binding interface of kinesin-4 KLP-12 at β-tubulin helix H12.
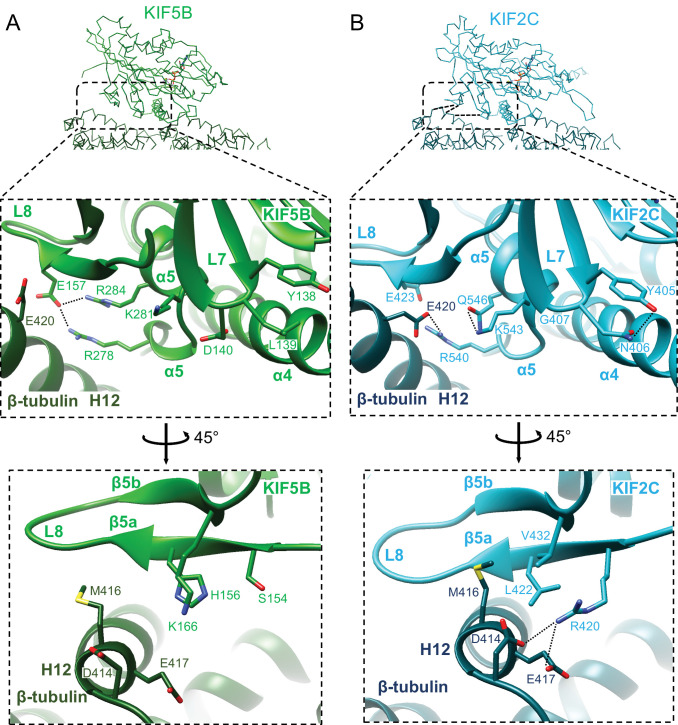
(A) Close-up display of KLP-12 and β-tubulin interaction around β-tubulin helix H12 from the same view as upper panel (middle panel) and 45° rotated view (bottom panel). Glu410 of β-tubulin H12 interacts with Arg311 and Arg317 of KLP-12 helix α5. Tyr150 and Asn151 of KLP-12 form intramolecular interactions. See Video 3 for detail. The interfaces of KIF5B and KIF2C at β-tubulin are available in Figure 5—figure supplement 1. (B) Sequence alignment with the secondary structure of the kinesin-4, KIF5B, and KIF2C residues at the interacting area. (C) Superimposition of Cα chain trace models of the KLP-12 complex (orange) and KIF5B complex (green) at kinesin around β-tubulin H12. (D) Superimposition of Cα chain trace models of the KLP-12 complex (orange) and KIF2C complex (cyan) at kinesin around β-tubulin H12.