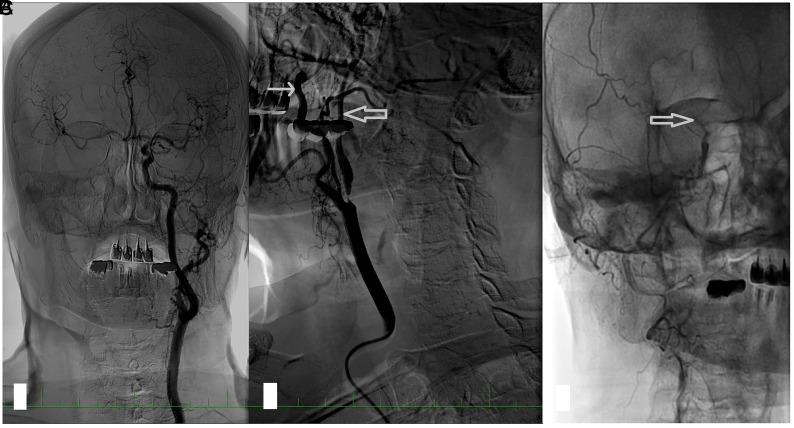
FIG 1.
An angiogram in a patient with right ICA near-occlusion. A, In a selective angiogram of the left carotid artery, no stenosis is present; the diameter of the ICA is larger than that of the ECA; and there is rapid filling of the intracranial circulation and intracranial collaterals to the right ACA and MCA. B, Near-occlusion of the right ICA. The diameter of the distal ICA (thick arrow) is smaller than that of the ECA (thin arrow) and much smaller than that of the contralateral ICA. Late filling of the distal ICA. C, In the late phase of the angiogram, the contrast filling stops at the level of carotid siphon (thick arrow). The intracranial circulation is not visualized because the contrast is diluted by collateral flow. ACA indicates anterior cerebral artery.