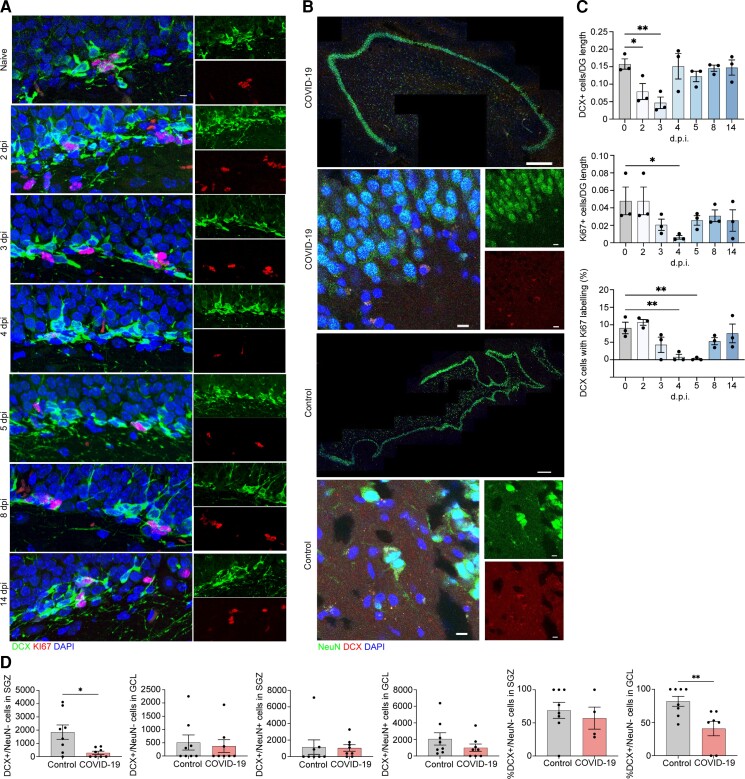
Figure 4.
Neuroblast proliferation in the SARS-CoV2 infected hamster and doublecortin (DCX)-positive cells and neurons in human hippocampus from COVID-19 patient and non-COVID-19 control. (A) Microscopy of the dentate gyrus of hamsters at naïve, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 and 14 dpi, showing staining of Ki67 (red), neuroblast (green) and DAPI (blue), followed by quantification of per cent Ki67+DCX+ cells, normalized to the total number of DCX+ cells. (C) Quantification of per cent DCX+Ki67+ area, normalized to total DCX+ area in the rostral migratory stream of hamsters at naïve, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 and 14 dpi. Data were pooled from at least two independent experiments. Scale bars = 50 μm. Data represent the mean ± SEM and were analysed by two-way ANOVA. (B) Select images of whole hippocampus and high-magnification images sections stained with DAPI (blue), NeuN (green) and DCX (red) from COVID-19 patient and non-COVID-19 control. The granule cell layer (GCL), subgranular zone (SGZ) and molecular layer (ML) of the dentate gyrus are visible, combined channels imaged at ×20; scale bar = 500 μm. High-magnification images were captured at ×63, scale bar = 20 μm. (D) In the SGZ, DCX+/NeuN− cells were fewer in COVID-19 patients versus controls [P = 0.026; t(7.794) = 2.731; Welch’s t-test for non-stoichiometric data], with no group differences in DCX+/NeuN+ cell number (P = 0.189; Mann–Whitney). In the GCL, neither DCX+/NeuN− cell count (P = 0.846; Mann–Whitney) nor DCX+/NeuN+ cell count (P = 0.378; Mann–Whitney) differs between COVID-19 and control subjects. Per cent of DCX+/NeuN− cells located in the SGZ versus the GCL did not differ between control and COVID-19 groups (P = 0.453; Mann–Whitney). Per cent of DCX+/NeuN+ cells located in the GCL versus the SGZ was lower in COVID-19 patients versus control subjects (P = 0.009; Mann–Whitney).