FIGURE 4.
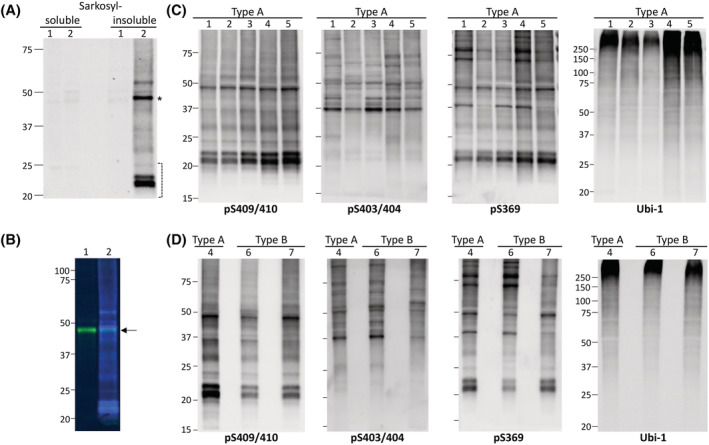
Isolation and biochemical characterisation of sarkosyl‐insoluble TDP‐43 in FTLD‐TDP Type A and Type B cases. (A) Representative Western blot (WB) of sarkosyl‐soluble and ‐insoluble fractions of a control (CTR) (1) and FTLD‐TDP Type A (2) case with pS409/410 antibody (Ab); phosphorylated TDP‐43 is only detected in the insoluble fraction of the Type A case. (B) Sarkosyl‐insoluble fractions from CTR (1) and FTLD‐TDP Type A (2) simultaneously immunoblotted with pS409/410 (blue) and C‐terminal pan TDP‐43 (green) Abs. A band of ~43 kDa (arrow) is observed in both preparations, corresponding to insoluble, non‐phosphorylated full‐length TDP‐43. TDP‐43 isolated from the frontal cortex of Type A (1–5) (C) and Type B (6 and 7) (D) cases immunoreacted with Abs targeting phosphorylated serines 409/410, 403/404 and 369, generating similar electrophoretic signatures within and between sets of samples. Ubiquitination affected mostly high molecular weight (MW) bands in all specimens; Ab: Ubi‐1. Asterisk indicates insoluble phosphorylated full‐length TDP‐43, and bracket indicates C‐terminal fragments (CTFs). Position and size (kDa) of MW markers are indicated on the left side of each WB
