Fig. 3: GATA4 knockdown in human iPS-CPs induces alternative splicing changes.
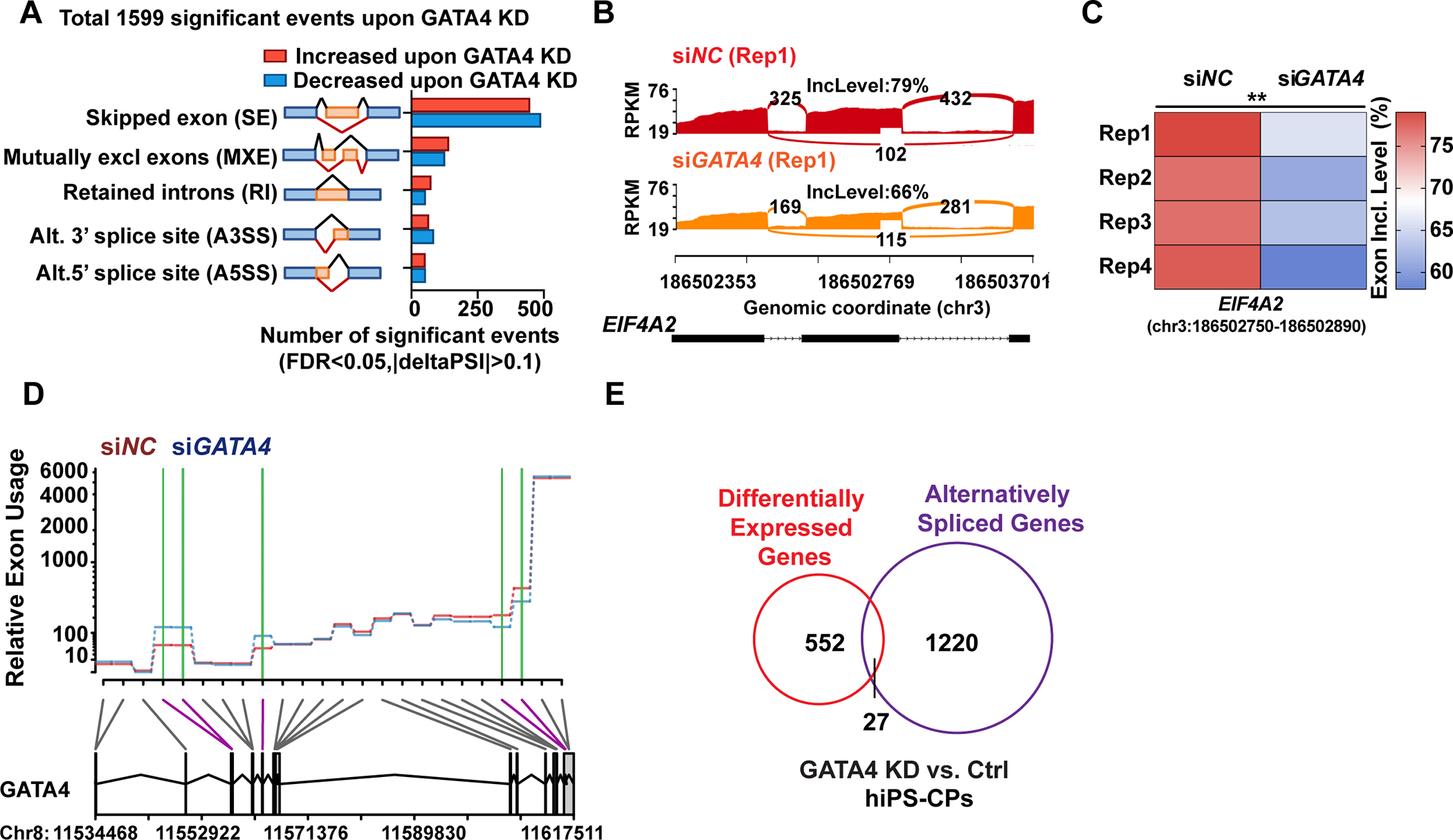
(A) Quantification of the alternative splicing events (n=1599) upon GATA4-knockdown (KD) by event type (FDR <0.05 from rMATS, junction counts ≥5) obtained from RNA-seq (n = 4). (B and C) Representative Sashimi plots depicting alternative splicing pattern of EIF4A2 in hiPS-CPs with siRNA targeting GATA4 (siGATA4) or negative control siRNA (siNC) and exon inclusion levels in each condition across four replicates (Rep). (D) Representative relative exon usage plots depicting alternative GATA4 splicing patterns in human iPS-CPs with green lines indicating change in exon inclusion upon GATA4 knockdown with siRNA compared to negative control siRNA. (E) Intersection of alternatively spliced genes upon GATA4-KD defined by rMATs (FDR <0.05, junction counts ≥5) and differentially expressed gene upon GATA4-KD (FDR<0.05, FC≥1.5).
