Fig. 5.
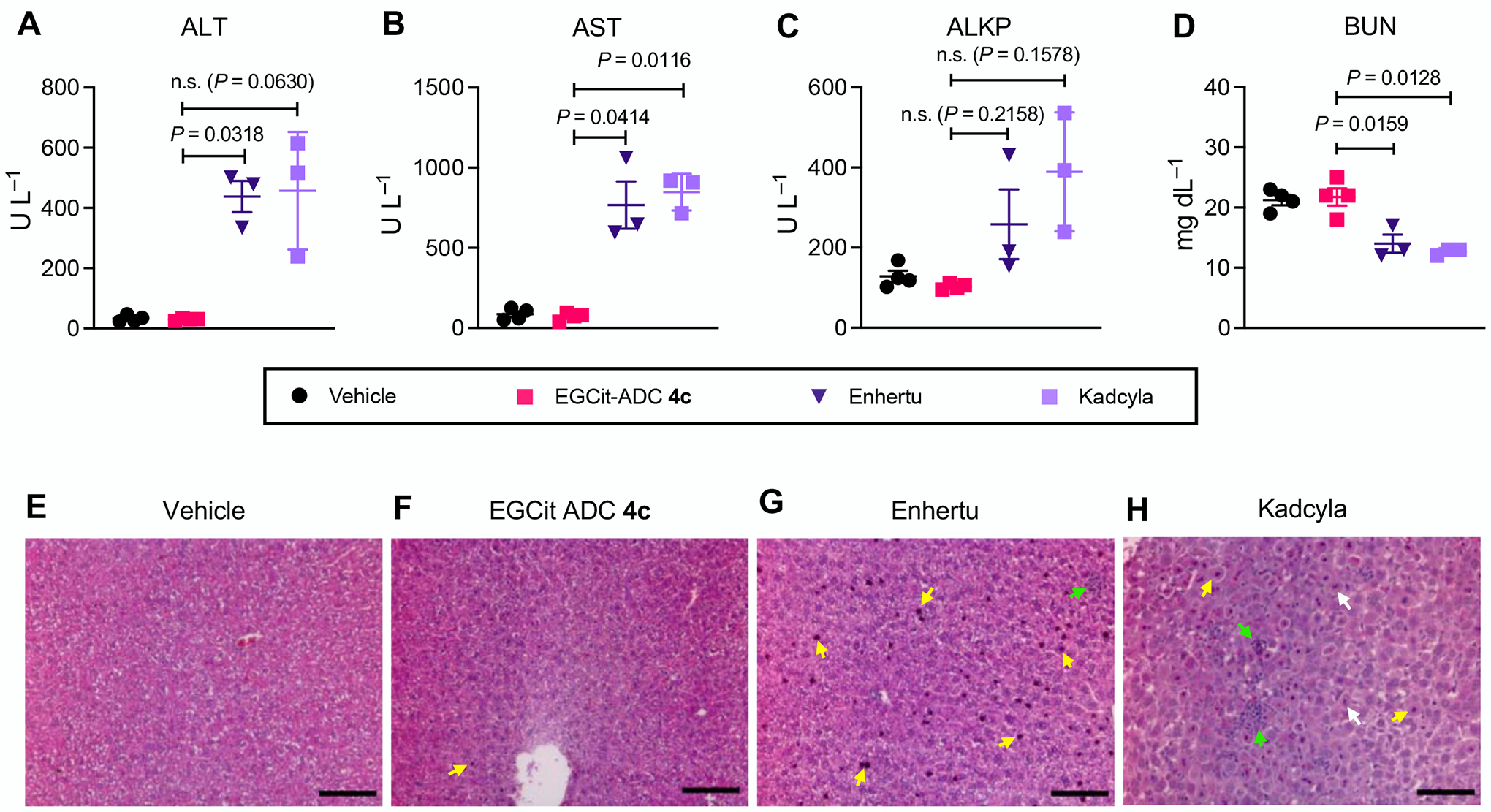
The EGCit linker has the potential to minimize antigen-independent hepatotoxicity of ADCs. A–D Blood chemistry parameters (ALT (A), AST (B), ALKP (C), and BUN (D)) measured 5 days post ADC injection to 6–8 weeks female CD-1® mice. Mice were injected intravenously with a single dose of vehicle control (n = 4), EGCit ADC 4c (magenta square, n = 4), Enhertu® (purple inversed triangle, n = 3), or Kadcyla® (light purple square, n = 3) at 80 mg kg−1. Data are presented as mean values (bars) ± SEM. For statistical analysis, a Welch’s t-test (two-tailed, unpaired, uneven variance) was used. To control the family-wise error rate in multiple comparisons, crude P values were adjusted by the Holm–Bonferroni method. E–H H&E-stained liver sections 5 days post treatment with vehicle (E), EGCit ADC 4c (F), Enhertu® (G), or Kadcyla® (H). Morphological changes are indicated with color arrows (yellow: condensed nuclei; green: necrosis and inflammation; white: fragmented nuclei). Scale bar: 100 μm. This experiment was repeated more than twice independently with similar results. ALKP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine transaminase; AST, aspartate transaminase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen, H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.
