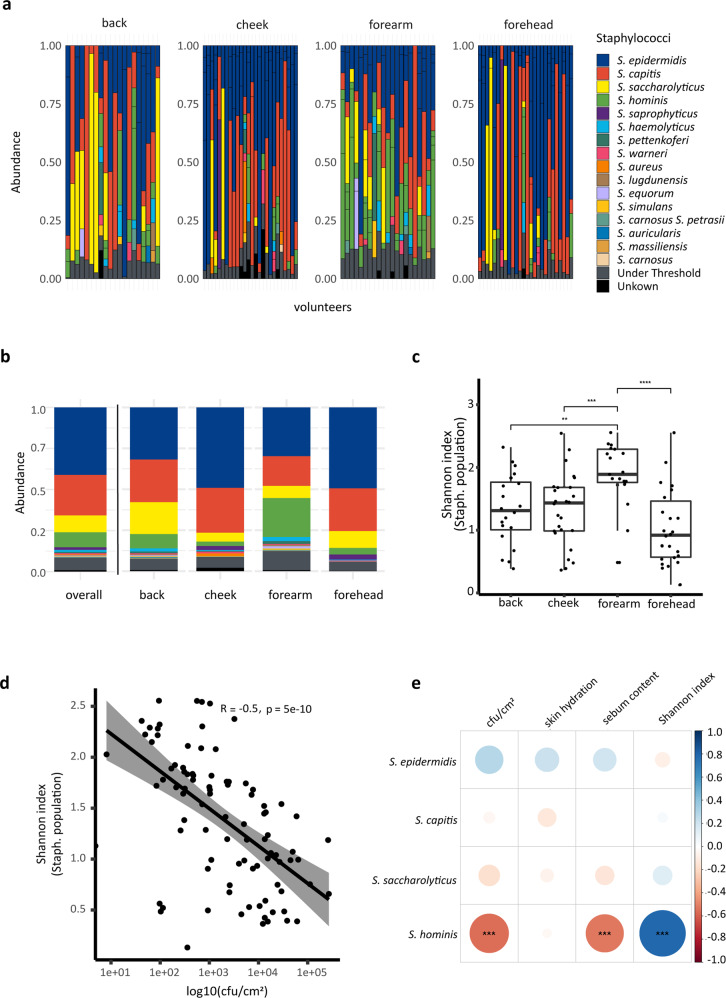
Fig. 2. Staphylococcal populations in skin samples determined by amplicon-based NGS and correlation to skin parameters.
a 93 out of 120 samples, obtained from 30 volunteers, were positive for the tuf2 amplification; relative abundance of staphylococcal species on back, cheek, forearm and forehead skin are shown (see also Supplementary Data 1). b Stacked bar plot showing mean values of relative abundances of staphylococcal species overall and for the four skin sites. c Shannon diversity index of staphylococcal population per skin site showed highest diversity in forearm skin samples (back skin samples, n = 20; cheek skin samples, n = 26; forearm skin samples, n = 21; forehead skin samples, n = 26. **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001. Unpaired Wilcoxon test). Middle lines of boxplots indicate the median. Lower and upper lines represent the first and third quartiles. Whiskers show the 1.5x inter-quartile ranges. d Spearman correlation between Shannon index of staphylococcal populations and CFU per cm2. e Spearman correlation between staphylococcal species abundance and skin parameters. The colour code illustrates the correlation coefficient; blue colour represents positive correlation (0 to 1) and red colour inverse correlation (−1 to 0). For instance, the presence of S. hominis strongly (and statistically significant) correlated with the Shannon index and inversely correlated with CFU count and with sebum content (FDR-adjusted p-value, ***p ≤ 0.001).