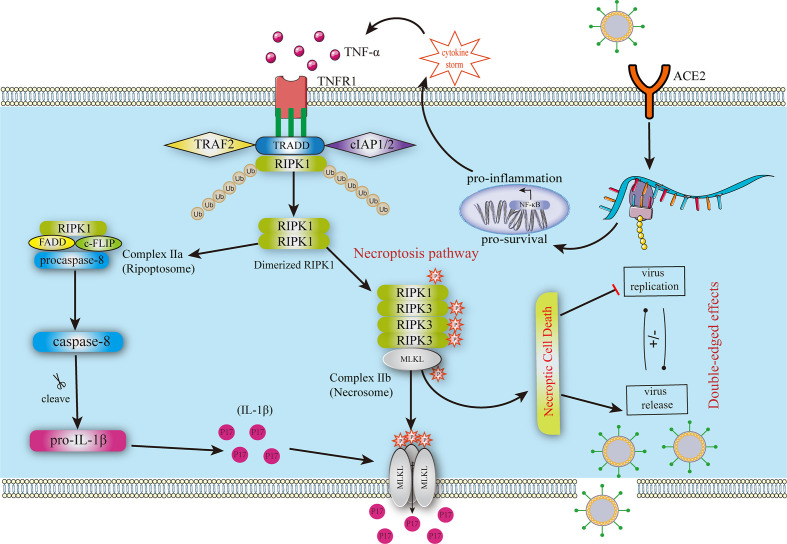
Figure 1.
Mechanism of necroptosis in COVID-19. The SRAS-CoV-2 infection leads to severe cytokine storms contributing to necroptosis in uninfected cells. TNF-α binds to TNFR1, forming a stable complex that deubiquitinates and includes complexes II A and II B Complex II b contains phosphorylated RIPK1, RIPK3, and MLKL, triggering the necroptosis pathway. MLKL is oligomerized to form pores in the membrane, leading to cytokine leakage. The other two pathways lead to caspase-8 production, including the RIPK1-independent and the RIPK1-dependent pathways. Then, caspase-8 promotes the production and leakage of IL-1β. FADD, FAS‐associated death domain; MLKL, pseudokinase similar to the mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase; RIPK1, receptor-interacting protein kinase 1; RIPK3, receptor-interacting protein kinase 3; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha; TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor receptor 1; TRADD, TNFR-associated death domain.