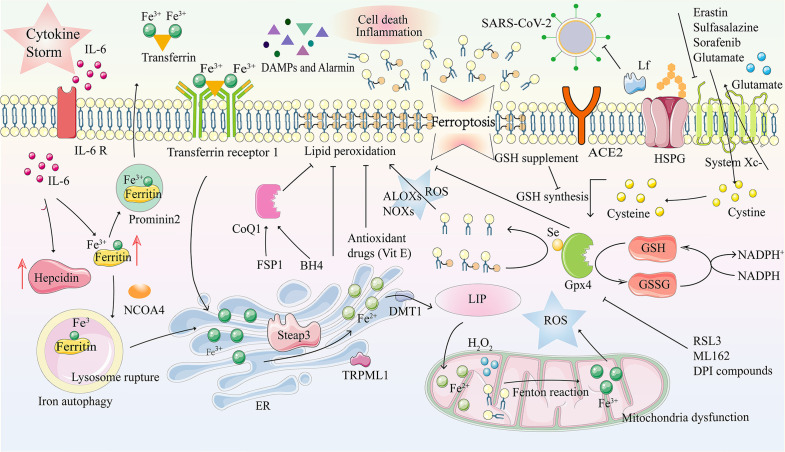
Figure 3.
Ferroptosis and its mechanism in COVID-19. Ferroptosis is a kind of programmed cell death characterized by an imbalance in intracellular iron metabolism or a distortion of the glutathione peroxidation pathway. The transferrin receptor recognizes excess transferrin carrying Fe3+ and enters cells through endocytosis after SARS-COV-2 infection. Metal reductase Steap3 reduces Fe ions from trivalent to divalent, while iron channels DMT1 and TRPML1 in the endosome membrane transport Fe2+ to the cytoplasm, accompanied by iron accumulation. In the case of intracellular iron overload, chemical substances in the mitochondrial electron transfer chain react with H2O2, Fe 2+, and lipids, together inducing the Fenton reaction, which produces large amounts of ROS. Due to GPX4 depletion and iron overload in LIP, lipid, nucleic acid, and protein peroxidation results in cell membrane damage due to oxidative stress and ferroptosis. DAMPs and Alarmin (HMGB1, IL-33, TNF) are released, eventually aggravating cell death and inflammation. Tf and prominin 2 can effectively excrete iron from cells and inhibit ferroptosis. ACE2R, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor; ALOXs, arachidonate lipoxygenases; BH4, tetrahydrobiopterin; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; DAMP, damage-associated molecular patterns; DFO, deferoxamine; DMT1, divalent metal transporter 1; DPI, diphenyleneiodonium; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor protein 1; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized GSH; HMGB1, high mobility group box-1 protein; HSPGs, heparan sulfate proteoglycans; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; IL, interleukin; Lf, lactoferrin; LIP, labile iron pool; LOXs, lysyl oxidases; NADP+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NCOA4, nuclear receptor coactivator 4; NOXs, NADPH oxidases; PLOOH, phospholipid hydroperoxide; PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; ROS, reactive oxygen species; RSL3, 1S,3R-RSL3; Se, selenocysteine; Steap3, six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3; TFR1, transferrin receptors 1; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TRPML1, transient receptor potential mucolipin 1; VitE, vitamin E.