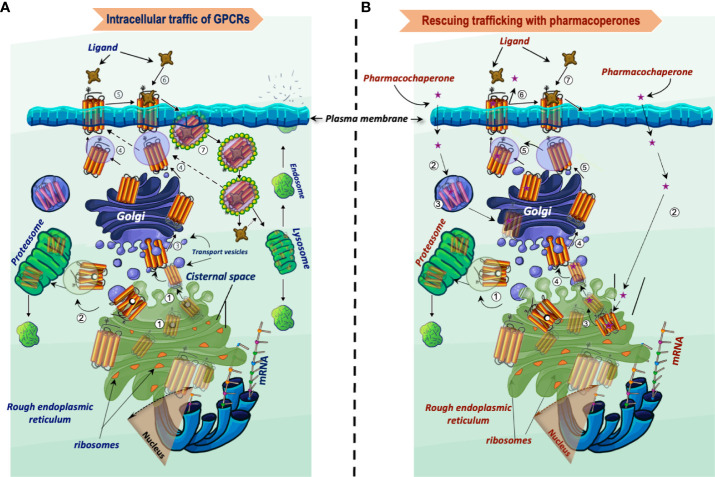
Figure 1.
Intracellular trafficking of GPCRs belonging to the rhodopsin-like family of receptors. (A) Newly synthesized proteins fold in the endoplasmic reticulum (step 1), where misfolded proteins interact with molecular chaperones and co-chaperones (oval black and white structures, respectively), which attempt to correct folding and stabilize the protein in a conformation adequate for endoplasmic reticulum export. When correction of misfolding fails, the abnormal protein is dislocated into the cytoplasm for proteasomal degradation (step 2). Folded GPCRs are translocated to the Golgi apparatus to complete their maturation process including glycosylation (arbor-like structure within the magnifier). Mature receptors then traffic to the plasma membrane where they bind their cognate ligands (steps 4 to 6). Following activation of the receptor by agonists, phosphorylation and recruitment of β-arrestins occur, which provoke endocytosis and internalization of the receptor–ligand complex (step 7). The internalized complex is embedded in clathrin-coated vesicles, which may be either targeted to lysosomes for degradation or dissociate with subsequent sorting of the receptor to the recycling pathway (step 4). (B) Rescue of misfolded receptors by pharmacoperones. Misfolded/misrouted receptors that could not be stabilized by molecular chaperones are submitted to degradation (step 1). The pharmacoperone drug crosses the cell surface plasma membrane, penetrates into the cell (step 2) and specifically binds the misfolded GPCR (step 3). Receptors stabilized by the pharmacoperone are then exported to the Golgi apparatus for further processing (step 4), and finally to the plasma membrane (step 5); here, the pharmacoperone (in the case of antagonists or agonists of the receptor) must dissociate from the rescued receptor for allowing the agonist to recognize and bind the rescued receptor promoting its activation (steps 6 and 7). Interaction of pharmacoperones with intracellularly trapped receptors also may occur in compartments other than the ER before degradation (step 3, left) (46).