Fig. 5.
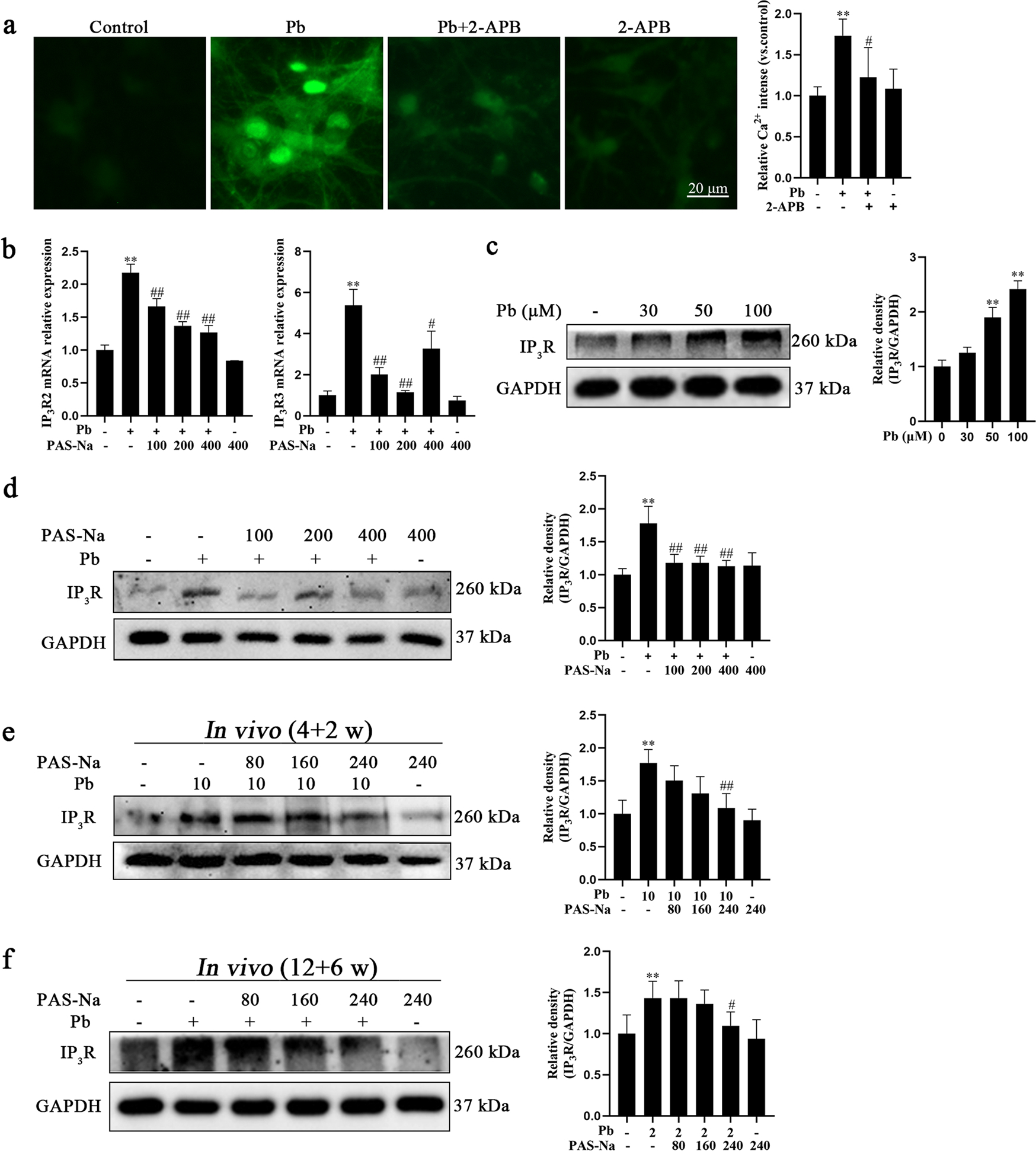
Pb-induced intracellular Ca2+ augment was associated with IP3R activation, which was blocked by PAS-Na. a Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with 50 μM PbAc in the presence or absence of pretreatment with 2-APB for 24 h. Representative fluorescent images of intracellular Ca2+ and quantifications of fluorescence intensity. Scale bar = 20 μm. b, d Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with 50 μM PbAc for 24 h, followed by 100, 200 or 400 μM PAS-Na treatment for 24 h. b The mRNA expressions of IP3R2 and IP3R3 were determined by RT-qPCR. c Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with increased concentrations of PbAc for 24 h. e Rats were treated with 10 mg/kg PbAc for 4 weeks during the juvenile period, followed by 80, 160 or 240 mg/kg PAS-Na treatment for 2 weeks. f Rats were treated with 2 mg/kg PbAc for 12 weeks, followed by 80, 160 or 240 mg/kg PAS-Na treatment for 6 weeks. c-f Protein level of IP3R was determined by western blotting. The protein expression was normalized by GAPDH. *P < and **P < 0.01, compared to the control group. #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01, compared to the Pb-treated group.
