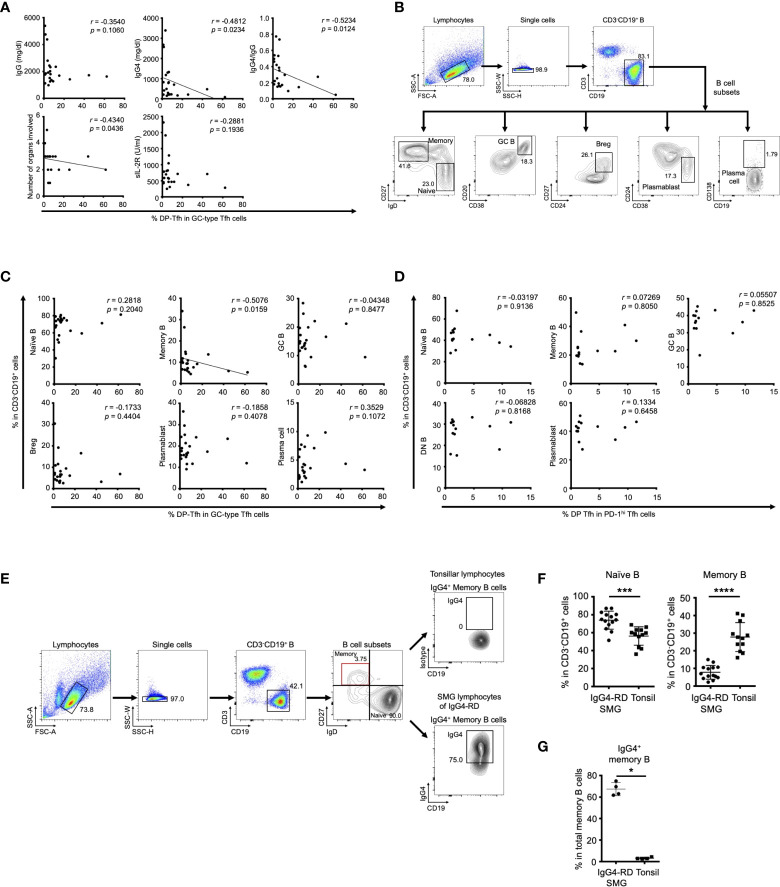
Figure 2.
Clinical association of DP-Tfh cells in IgG4-RD lesions. (A) Scatter plots showing relationships between various clinical parameters associated with the IgG4-RD disease state and the ratios of DP-Tfh cells (CD3+CD4+CD8+CXCR5hiPD-1hi) to total GC-type Tfh cells (CD3+CD4+CXCR5hiPD-1hi) in SMG lesions of IgG4-RD (n = 22). (B) Flow cytometry profiles showing selected windows and gating strategies applied to identify B cells (CD3-CD19+) and B-cell subsets (naïve B cells, CD3-CD19+IgD+CD27-; memory B cells, CD3-CD19+IgD-CD27+; GC B cells, CD3-CD19+CD20+CD38+; regulatory B cells, CD3-CD19+CD24hiCD27+; plasmablasts, CD3-CD19+CD24-CD38+; plasma cells, CD3-CD19+CD138+) in SMG lesions of IgG4-RD. (C) Scatter plots indicating the relationships between the ratios of various B-cell subsets and ratios of DP-Tfh cells to total GC-type Tfh cells in SMG lesions of IgG4-RD (n = 22) measured by flow cytometry. (D) Scatter plots indicating relationships between the ratios of various B-cell subsets and ratios of DP-Tfh cells to total GC-type Tfh cells in tonsils (n = 14) measured by flow cytometry. (E) Flow cytometry profiles showing selected windows and gating strategy for IgG4-expressing memory B cells of lymphocytes of tonsils and SMG lesions of IgG4-RD. (F) Naïve and memory B cells in SMG lesions of IgG4-RD (n = 14) and tonsils (n = 12) analyzed by flow cytometry. (G) High frequency of memory B cells expressing IgG4 (IgG4+ memory B cells) in SMG lesions of IgG4-RD analyzed by flow cytometry (IgG4-RD, n = 4; tonsil, n = 4). Data in (A, C, D) were analyzed by the Spearman’s rank correlation test, and data in (F, G) were studied by the Mann–Whitney U test.