Figure 5.
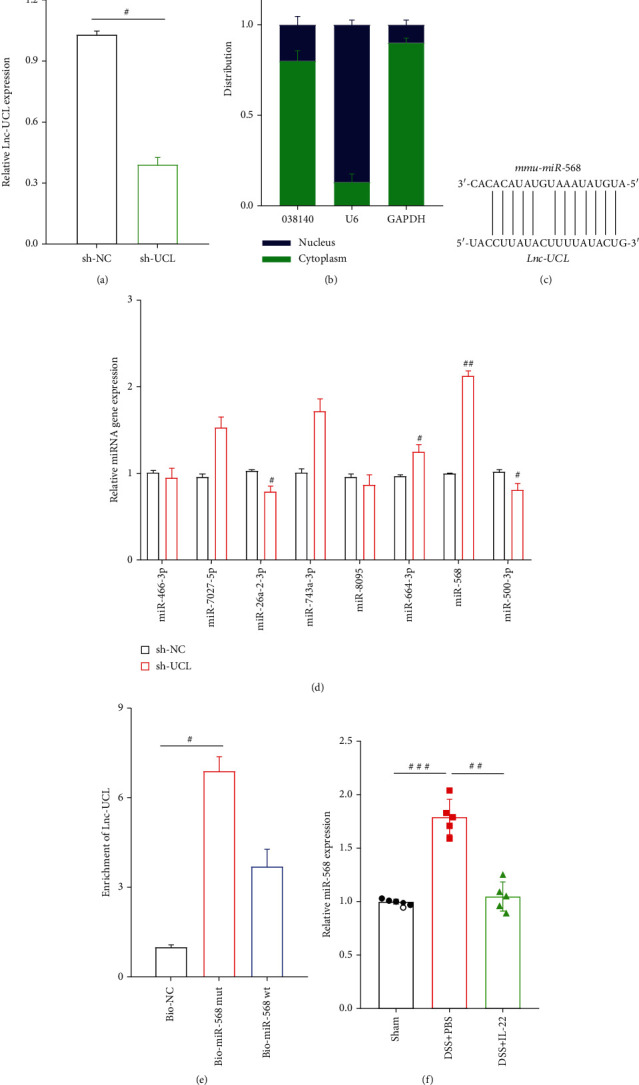
lncRNA-UCL is predominantly located in the cytoplasm and binds to miR-568 in intestinal epithelial cells. (a) The interfering sequence that could specifically target lncRNA-UCL was inserted into the vector, and the lentivirus was constructed to detect interfering efficiency. (b) qRT-PCR analysis of lncRNA-UCL expression in the nuclear and cytosolic components of MODE-K cells. (c) Sequence alignment showing the binding sites between miR-568 and lncRNA-UCL. (d) After the silencing of lncRNA-UCL expression, qRT-PCR analyzed the changes in miRNA expression, to identify miRNAs that may bind to lncRNA-UCL in MODE-K cells. (e) RNA-pulldown assay was conducted to detect interactions between miR-568 and lncRNA-UCL. (f) qRT-PCR was performed to measure miR-568 expression in colon tissues among all groups of mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. ###P < 0.001; ##P < 0.01; #P < 0.05 using Student's t-test.
