Fig. 3.
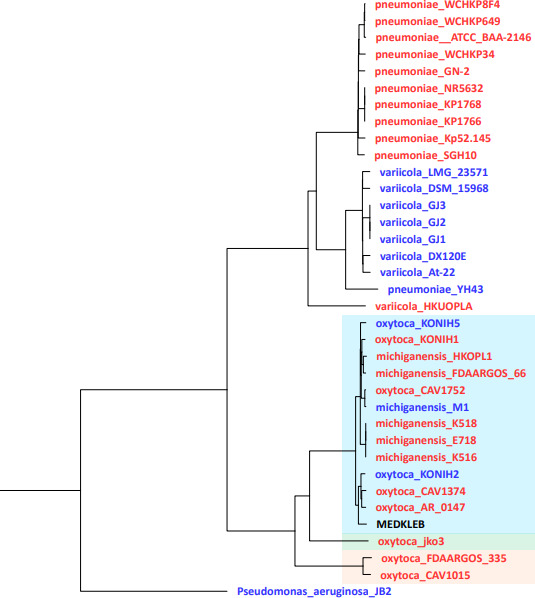
ANI hierarchical clustering showing the evolutionary relationship of environmentally-derived and host-derived Klebsiella bacteria. The tree was created using the ANI calculator [75], with Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain JB2 selected as the outgroup. Bacteria derived from animal hosts (red and black), and environmentally derived bacteria (blue), generally fell into three clades: 1) K. pneumoniae , 2) K. variicola and 3) K. oxytoca/michiganensis. With one exception in each group (YH43 and HKUOPLA), all K. pneumoniae are host derived and all K. variicola are environmentally derived. K. oxytoca/K. michiganensis have been isolated from both environmental and animal sources, but their sequences did not cluster according to source status. According to the ANI species threshold set by Kim et al. [105], Medkleb is conspecific with twelve strains in the ‘Medkleb group’ which have been classified on the RefSeq database as both K. oxytoca and K. michiganensis . However, Kleborate [77] identified all strains in the Medkleb group (bounded within a blue box) as K. michiganensis, the single strain bounded in a green box as K. grimontii and the two strains bounded in an orange box as K. oxytoca .
