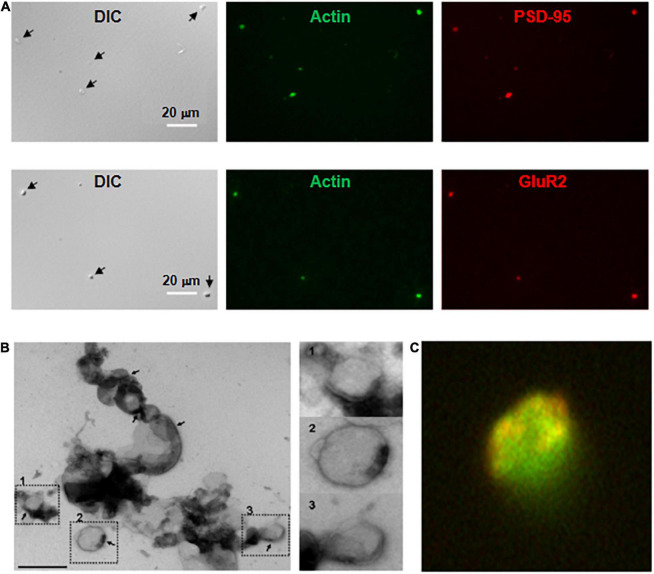
FIGURE 2.
Imaging and immunocytochemical analysis of isolated DS. (A, Top) Isolated DS were identified by DIC (×60) and recognized by their “wrinkled sac” shape, of approximately 1 μm diameter. Labeling of fresh (not-fixed) DS allowed identification of abundant intra-DS F-actin (FITC-phalloidin, Green) and PSD-95 (Cy3, Red). (Bottom) Similar approach as in (Top), but co-localization of glutamate receptor GluR2 (Cy3, Red) and FITC-phalloidin to identify F-actin (Green) (×60). (B) Negative staining of freshly isolated DS labeled with phosphotungstic acid. Large clusters of individual DS were often identified. However, it is expected that clustering may be a consequence of negative staining. In particular, PSD were observed in several membranes (marked in numbers), with a clear intravesicular content, as expected from DS and not synaptosomes. Right, higher magnification imaging shows DS of different sizes. (C) DS with the shape features of the membrane and abundant filamentous material depicting to the open left, identified as polymerized actin (Green). Isolated DS often showed clearly defined PSD (×50,000).