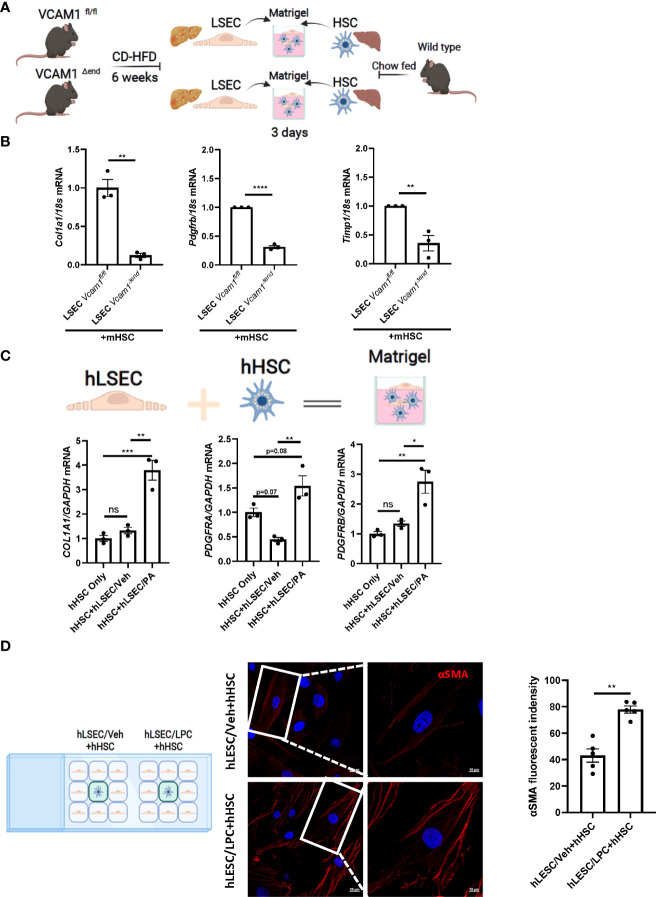
Figure 2.
Lipotoxic LSECs activate HSCs during NASH in a VCAM1 dependent manner. Primary LSECs were isolated from Vcam1Δend or Vcam1fl/fl mice with NASH and primary HSCs were isolated from healthy wild type mice and co-culured using 3-D co-culture sytem. (A) Schema of the 3-D coculture system used for mouse primary cells co-culture. (B) mRNA levels of HSCs activation markers, Col1a1, Pdgfrb and Timp1 were assessed by real-time PCR. Fold change was determined after normalization to 18s rRNA. n=3. (C) Human primary LSECs and HSCs were co-cultured using the same 3-D co-culture system. hLSECs treated with vehicle or palmitate (PA) 500 μM overnight then co-cultutred with hHSCs for 3 days in LSEC growth medium without PA treatment, HSCs activation was examined by mRNA expression of COL1a1, PDGFRA and PDGFRB. n=3. (D) hLSECs and hHSCs were co-cultured using a 2-D co-culture μ-slide to examine the effect of hLSECs-derived soluble factors on hHSCs activation. hLSECs in the peripheral wells were pre-treated with LPC 20μM for 4 hours, then LPC containing media was replaced and filled up to allow for intercellular communication via soluble factors. After 6-hours of co-culture, hHSCs activation was examined by αSMA staining. Scale bar: 20μm left pannel, 10μm right pannel. αSMA fluorescent density from 5 random fields was quantified using ImageJ software. *, **, ***, **** indicate statistical significance with p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < 0.001 and p < 0.0001, respectively. Statistically non-significant results were labeled as ns.