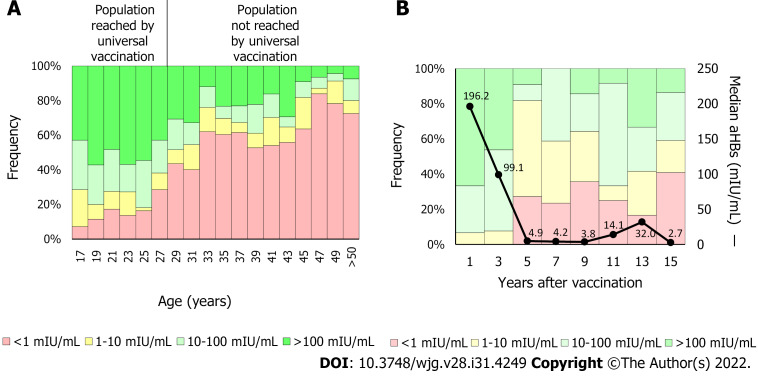
Figure 3.
Anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies titers by age. A: The anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies (anti-HBs) titer was determined in 765 blood donors. In 2000, vaccination against hepatitis B virus was included in the Argentine newborns’ National Vaccination Calendar. In 2003, the catch-up strategy for 11-year-old children was implemented. Therefore, individuals under 28-years-old are reached currently by the universal vaccine implementation. On average, protective levels of anti-HBs (> 10 mIU/mL) were detected in 75.2% of the population reached by universal vaccination (< 28-years-old) and in 32.2% of the not reached population (> 28-years-old); B: Anti-HBs kinetics. The anti-HBs titer was determined in 132 children born after 2000. In the first 2 years, the median anti-HBs titer fell from 196.2 mIU/mL to less than 10 mIU/mL (black line). Five years post-vaccination, about 20% of the population showed anti-HBs levels below 10 mIU/mL. aHBs: Anti-hepatitis B surface antibodies.