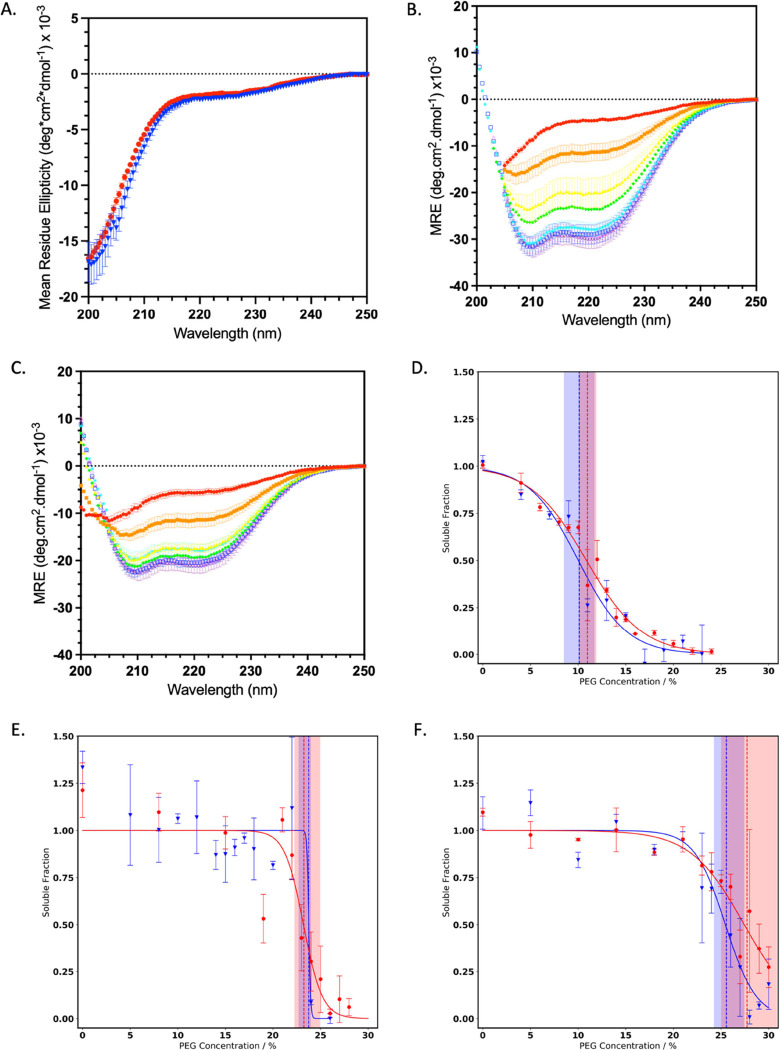
Figure 3.
Structural properties and the solubility of monomeric α-synuclein are only slightly affected by N-terminal acetylation. (A) Far UV CD spectra of non-acetylated α-synuclein (blue triangle) and N-terminal acetylated α-synuclein (red dot) monomers; error bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM) with n = 3 (B, C) CD spectra of non-acetylated α-synuclein (B) and acetylated α-synuclein (C), in the presence of increasing concentrations of DMPS: 0.1 mM (red), 0.25 mM (orange), 0.5 mM (yellow), 0.75 mM (green), 1 mM (cyan), 1.5 mM (blue), 2 mM (lilac), and 3 mM (purple); MRE, and error bars represent the SEM with n = 3. (D–F) Solubility of monomeric α-synuclein was measured by incubation with increasing concentrations of PEG at pH 4.8 (D), pH 6.5 (E), and pH 7 (F) for non-acetylated α-synuclein (blue) and acetylated α-synuclein (red). The dashed lines represent the PEG1/2 value (which is correlated with the solubility) with confidence intervals represented by shaded areas; error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM).