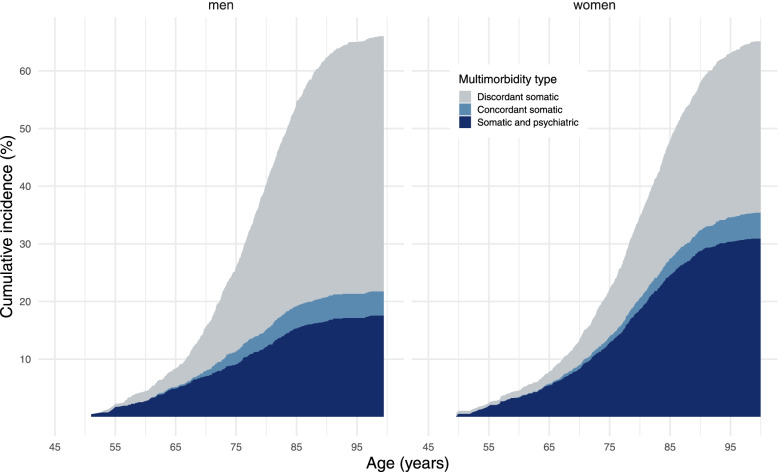
Fig. 3.
Lifetime risk of multimorbidity for men and women over 45 years free of the ten selected diseases at baseline. In this analysis, follow-up ended at the time of diagnosis of the second medical disease of interest, at the time of death, or at the time of censoring or at the end of the administrative study period. The three types of multimorbidity are based on the combinations of the first two diseases in chronological order. All combinations of diseases that involve depression were classified as somatic-psychiatric multimorbidity; all other combinations as somatic multimorbidity. Combinations of somatic diseases that affect the same organ system were classified as somatic concordant, combinations of somatic diseases affecting different organ systems were classified as somatic discordant. Somatic concordant multimorbidity involved the combinations of COPD and asthma, coronary heart disease and heart failure, and parkinsonism and dementia. All other pairs of individual diseases were classified as somatic discordant