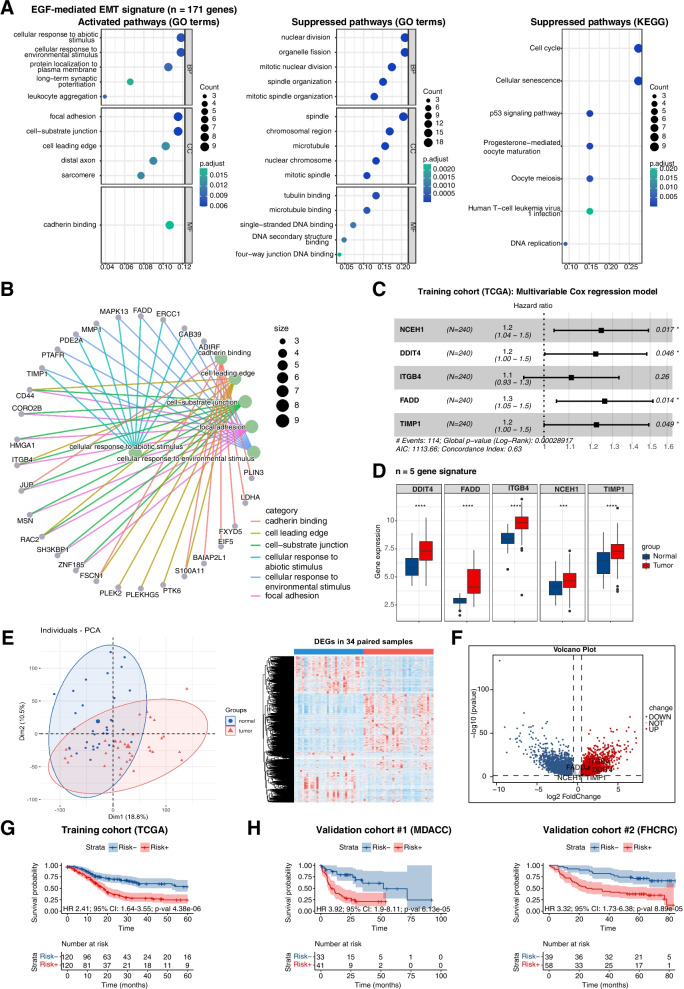
Fig. 4.
EGFR-mediated EMT-dependent 5-gene prognostic signature for HNSCC. A Genes of the EGFR-mediated EMT signature (n = 171) were subjected to an over-representation analysis. Significantly activated and suppressed pathways in GO and KEGG are depicted with gene counts and adjusted p-value. B Genes from the enriched GO-terms are depicted in a gene-concept network. C Forest plot of the multivariable Cox PH regression model incorporating the 5-gene signature in the training cohort (TCGA) of n = 240 HPV-negative HNSCC with event numbers, log-rank p-value, AIC, and concordance index. D Gene expression of DDIT4, FADD, ITGB4, NCEH1, and TIMP1 in normal mucosa (n = 34) and HNSCC (n = 238) of the training cohort (TCGA); p-values *** ≤ 0.001; **** ≤ 0.0001. E Principal component analysis and hierarchical clustering of the top 25% most strongly regulated DEGs for matched pairs of normal mucosa and HNSCC of the TCGA cohort are shown (n = 34). F Volcano plot of DEGs from matched pairs of normal mucosa and HNSCC of the TCGA cohort (n = 34; |log2FC|> 0.5, p-value ≤ 0.05). Genes of the 5-gene signature are significantly up-regulated DEGs. G Stratification of HPV-negative HNSCC of the training cohort (TCGA; n = 240) with a 5-gene signature-based risk score (median cut-off) for overall survival (time in months). Numbers at risk, HR, 95% CI, and p-value are indicated in the Kaplan–Meier survival curve. H Validation of the risk score in the MD Anderson Cancer Center (MDACC; n = 74) and the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center (FHCRC; n = 97) HNSCC cohorts. Median cut-off threshold of the training cohort served to dichotomize the MDACC and FHCRC cohorts (risk − , risk +) for overall survival. Numbers at risk, HR, 95% CI, and p-value are indicated in the Kaplan–Meier survival curve