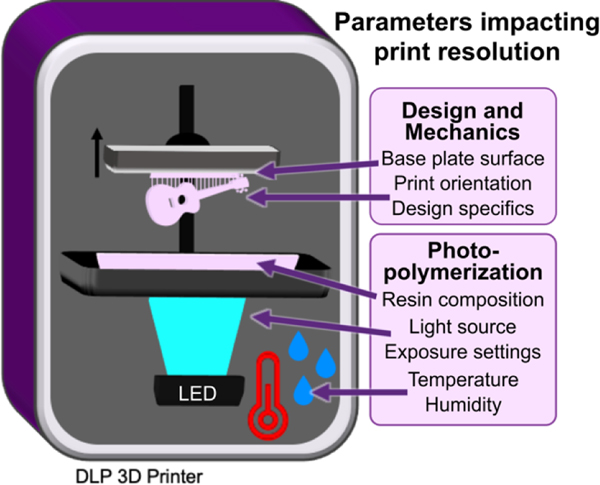
Fig. 1.
Schematic of a DLP 3D printer, highlighting the design and mechanical factors as well photopolymerization parameters which influence print resolution. Digital light processing 3D printers project UV or violet light through optically clear sheets (usually Teflon) into a vat of photopolymerizable resin (pink). In locations where the light is projected, the resin crosslinks to form a solid structure. Exposure and crosslinking are performed layer by layer on the base plate, which lifts up as each concurrent layer is formed. Production of a clean print is dependent on instrumental, environmental, chemical, and design elements that impact either the print surface (base plate), mechanics (print orientation, design specifics), or chemical reaction (resin composition, light source, exposure settings, temperature, or humidity).