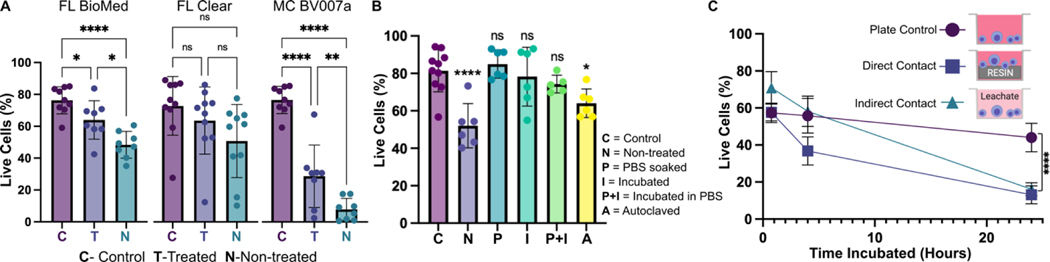
Fig. 7.
Viability of primary murine splenocytes in contact with 3D printed materials. Primary splenocytes from male and female mice (Nmice = 2 per experiment) were evaluated by flow cytometry after live/dead staining with Calcein-AM/7AAD. (A) Cell viability after 4 hr of direct physical contact with PBS+incubation treated (T) or non-treated (N) resins compared with well plate control (C). Treated BioMed and Clear prints maintained relatively high viability compared to the well plate, while BV007 did not. Bars show mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA per data set, ns > 0.06, *p > 0.01, **p = 0.01, ****p < 0.0001. (B) Multiple post-treatment methods (PBS, incubation at 37 °C, PBS+incubation, and autoclavation) were evaluated using BioMed resin and culturing for 4 hours with direct contact. Bars show mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA, ns > 0.2, *p > 0.02. ****p < 0.0001. (C) Viability of direct contact (i.e. culture with resin) and indirect contact (i.e. culture with resin leachate) of cells with treated BioMed prints at 45 min, 4 hours, and 24 hours showed a decrease in viability over time. Values show mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA at final time point, ****p < 0.0001.