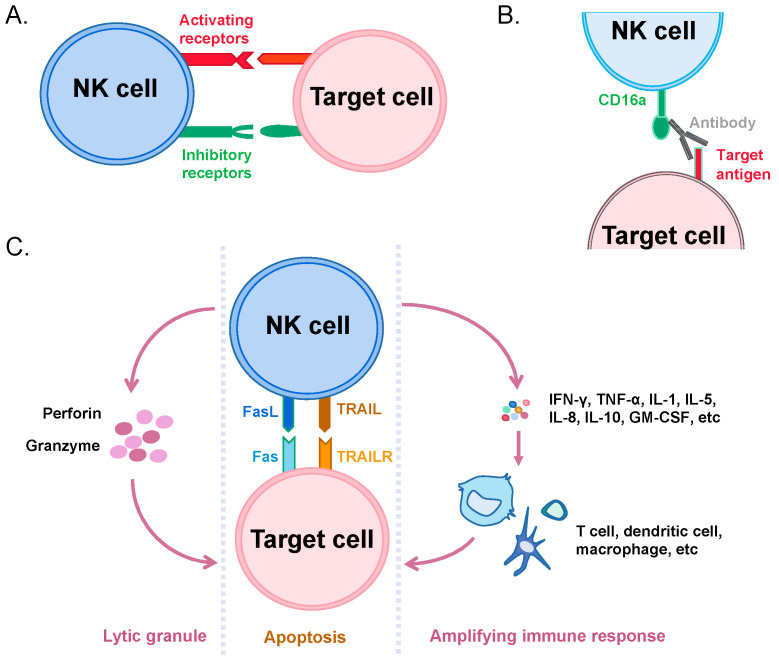
Figure 2.
Cartoon illustration of NK cell activation and cytotoxicity. (A) NK cell can bind to target cell through both activating receptors (red) and inhibitory receptors (green). Its status is dependent on which signaling is dominant. (B) NK cell can also be activated through its CD16a binding to a cell-bound antibody. (C) Activated NK cells kill target cells through the release of lytic granules and FasL-Fas/TRAIL-TRAILR axis. NK cells also recruit other immune cells through the cytokine release to amplify the immune response against target cells.