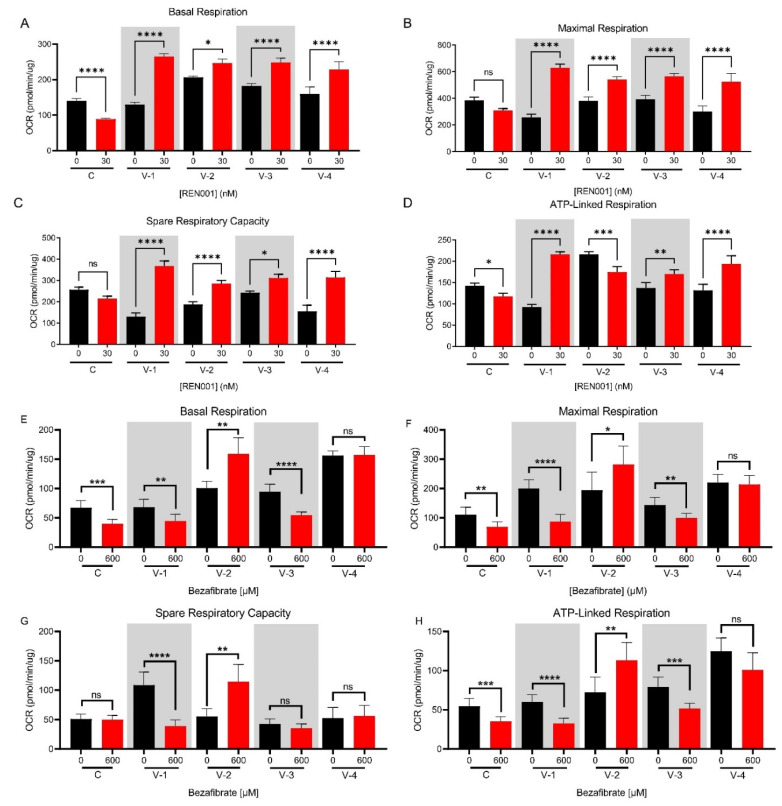
Figure 4.
Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) of control and VLCAD-deficient cell lines treated with REN001 for 48 h (A–D). Briefly, basal respiration is the OCR of the cells under baseline conditions. Maximal respiration is the OCR measured by exposing the cells to carbonyl cyanide-4 (trifluoromethoxy) phenylhydrazone (FCCP), which is an uncoupling reagent that collapses the proton gradient and disrupts mitochondrial potential. Electron flow through the electron transport chain is disrupted and complex IV reaches the maximum OCR. Spare respiratory capacity is the cell’s ability to respond to stress via exposure to rotenone and antimycin (ROT/AA; complex I and II inhibitors, respectively). ATP production is the decrease in OCR via exposure to ATP synthase inhibitor (complex V), oligomycin, and represents the portion of basal respiration used to drive ATP production. Basal respiration (A), maximal respiration (B), spare respiratory capacity (C), and ATP production (D). Oxygen consumption rate of control and VLCAD-deficient cell lines treated with bezafibrate (BEZ) for 48 h (E–H). Basal respiration (E), maximal respiration (F), spare respiratory capacity (G), and ATP production (H). Bars represent mean and standard deviations in duplicate assays. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p <0.001, **** p < 0.0001, ns = no significant, compared to each cell line’s own 0 nM treatment (n = 6 for all assays; t-test for unpaired samples).