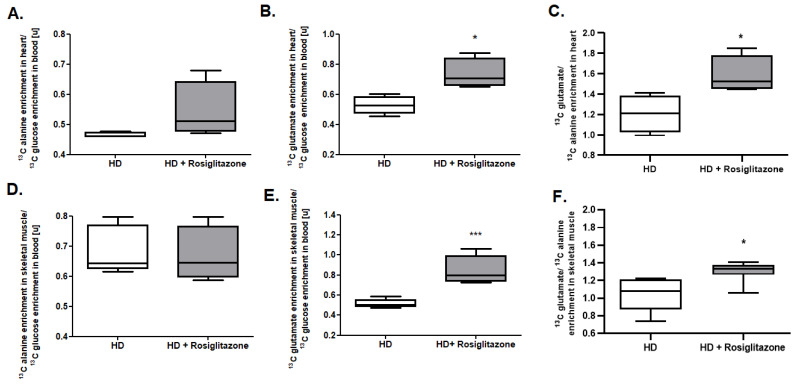
Figure 3.
Increased glucose usage in cardiac and skeletal muscle metabolism in Huntington’s disease (HD) mouse model treated with rosiglitazone. (A) 13C alanine enrichment in heart/13C glucose enrichment ratio in the blood, (B) 13C glutamate enrichment in heart/13C glucose enrichment ratio in the blood, (C) 13C glutamate/13C alanine enrichment ratio in the heart, (D) 13C alanine enrichment in skeletal muscle/13C glucose enrichment ratio in the blood, (E) 13C glutamate enrichment in skeletal muscle/13C glucose enrichment ratio in the blood, (F) 13C glutamate/13C alanine ratio enrichment in the skeletal muscle of R6/1 (HD) and R6/1 with rosiglitazone treated mice (HD + Rosiglitazone). Data presented; n = 5; * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001. Due to the methodological inability to compare the obtained values with previous experiments, values from control experiments (wild-type mice) are not shown. Nevertheless, the comparison of glucose usage in cardiac and skeletal muscle metabolism between control and HD mice models was already published in our two previous studies [17,30].