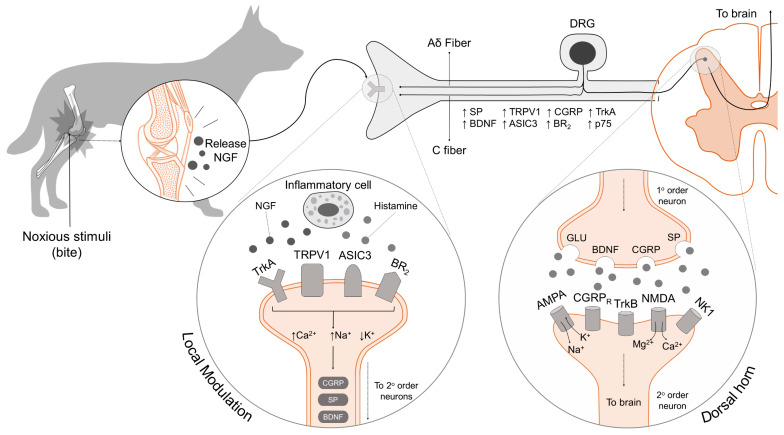
Figure 6.
Sensitization of the nervous system. Inflammatory mediators (histamine, NGF) released after tissue injury (bites) bind to peripheral receptors located on first-order neurons. Activation of these receptors (TrkA, TRPV1, ASIC3, BR2) and ionic channels, such as Na+, Ca2+ and K+, modulates and enhance the excitability of the primary afferent nerve cells. When the nociceptive signal reaches the dorsal horn of the spinal cord, it causes the release of pronociceptive neurochemicals including GLU, SP, CGRP, and BDNF, from the primary neurons to the second-order neuron receptors, mainly AMPA, NMDA, NK1, CGRPR, and TrkB. These receptors promote the transmission of the excitatory signaling to the brain and cortical structures, where the perception of pain is consciously recognized. Abbreviations: AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic; ASIC3: acid-sensing ion channel 3; BDNF: brain-derived neurotrophic factor; BR2: bradykinin receptor 2; CGRP: calcitonin-gene-related peptide; DRG: dorsal root ganglion; GLU: glutamate; NGF: nerve growth factor; NK1: neurokinin 1 receptor; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate; p75: neurotrophin receptor; SP: substance P; TrkA: tropomyosin kinase receptor A; TRPV1: transient potential receptor vanilloid 1. DeLeo [66], Verri et al. [67], Watkins et al. [68], and Enomoto et al. [69].