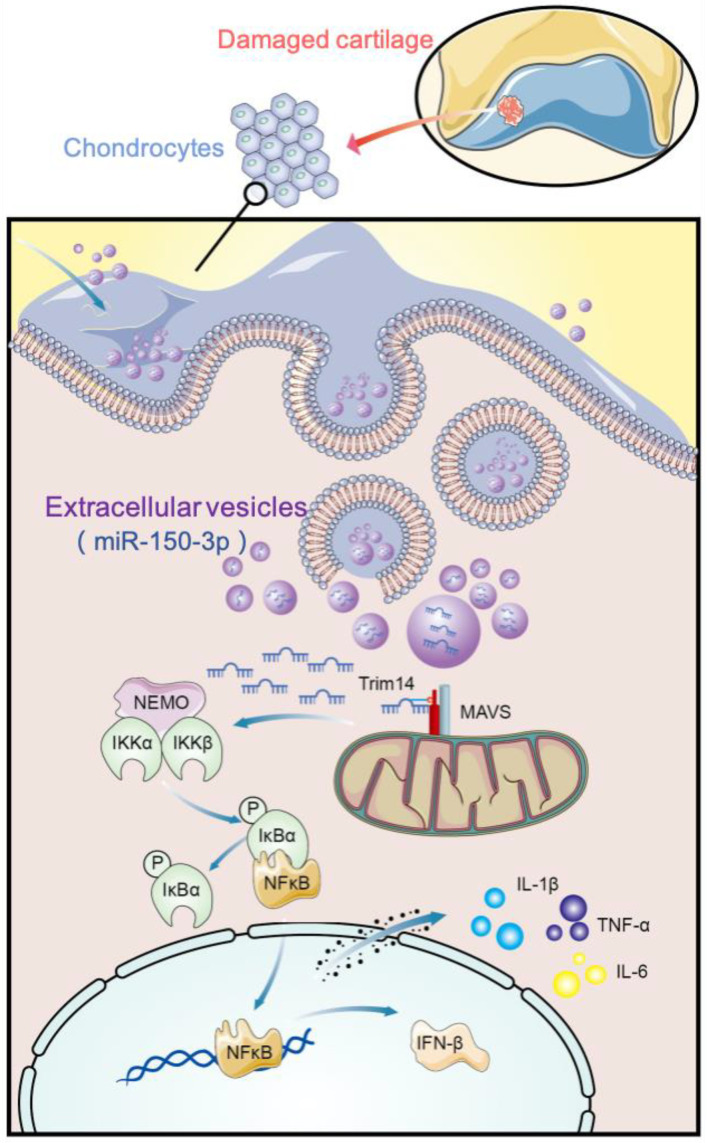
Figure 13.
Therapeutic mechanisms of FLS-derived EVs-150. EVs released by the FLSs in the healthy SM were collected, and these EVs could deliver miR-150-3p to chondrocytes. When OA occurs, Trim14 is recruited to the IKK complex by binding to NEMO, a large multi-unit complex that consists of two catalytic subunits (IKKα and IKKβ) and the regulatory subunit IKKγ (which is also known as NEMO, an essential modulator of NF-κB expression). IKK promotes the phosphorylation of IκBα and p65 as well as NF-κB activation and IFN-β expression. After the immune response was activated, the primary pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α were expressed, and the various cytokines and chemokines were synthesized and released. Some of these inflammatory mediators were detected in the joint tissues and synovial fluid of OA rats. These mediators can accelerate chondrocyte degradation and metabolism, thereby injuring the joint and causing a series of clinical symptoms. EVs-150 from healthy FLSs could regulate the mRNA level of the target gene Trim14, thereby effectively inhibiting the activation of the positive feedback loop formed by the Trim14/NF-κB/IFN-β axis of the innate immune response, consequently exerting a suppressive effect on the OA processes indicated above.