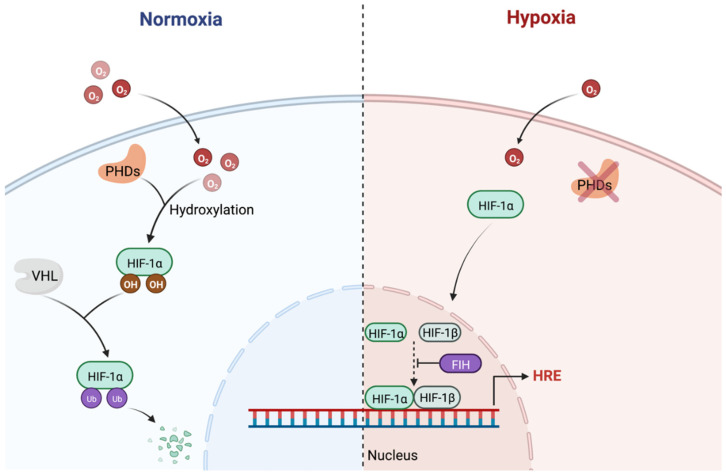
Figure 1.
The HIF degradation pathway. Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α undergoes hydroxylation via PHDs which require oxygen. This hydroxylation allows HIF to be preferentially recognised by the VHL protein which targets the protein for ubiquitylation-dependent proteasomal degradation. In hypoxic environments, HIF-1α is not targeted for hydroxylation and degradation, therefore accumulates and is translocated into the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, it can form a heterodimer with HIF-1β which binds to the hypoxia response elements (HRE) on the target genes to initiate their transcription. Figure created with BioRender.com (accessed on 13 July 2022).