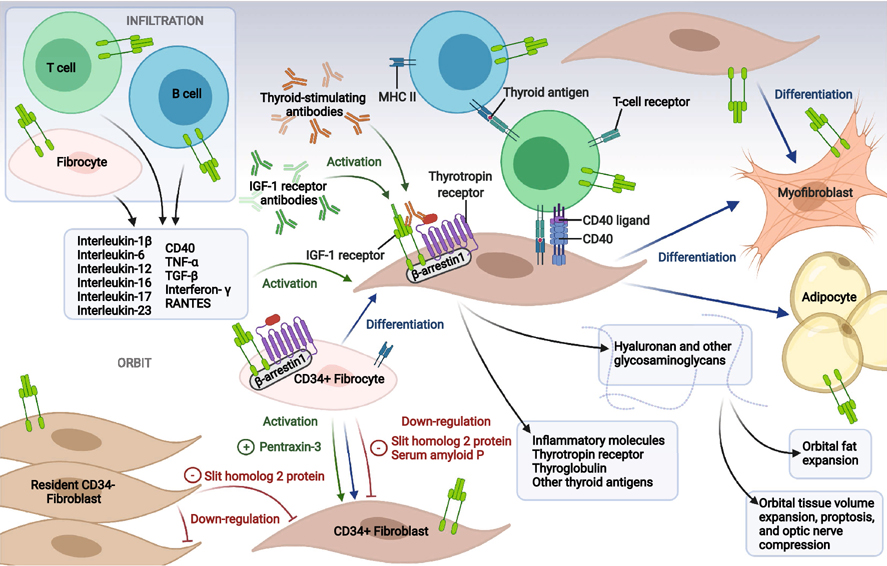
Figure 1.
Theoretical concept of TAO pathogenesis. CD34+ fibrocytes of the monocyte lineage infiltrate the orbit where they can differentiate into CD34+ fibroblasts, adipocytes, and myofibroblasts. CD34+ fibroblasts co-populate the orbit with CD34− fibroblasts in an admixture (GD-OF). CD34+ fibrocytes express thyroid autoantigens, including thyrotropin receptor (TSHR), thyroglobulin (Tg), thyroperoxidase (TPO), and sodium-iodide symporter (NIS), the expression of which depends on the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) protein. Fibrocytes can present antigens to T cells which in turn support IgG1 production in B cells. When activated, fibrocytes and orbital fibroblasts produce many cytokines, including interleukins 1β, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 23, TGF-β, tumor necrosis factor α, regulated on activation, normal T expressed and secreted (RANTES,) CXCL-12 and CD40 ligand (CD154). Many genes expressed by fibrocytes are also detected in CD34+ fibroblasts but at considerably lower levels. These lower levels result from actions of Slit2 which is expressed and released by CD34− orbital fibroblasts. Orbital fibroblasts display the tyrosine kinase, insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR), a therapeutic target for TAO. Cytokine-activated orbital fibroblasts express all three mammalian hyaluronan synthase isozymes and UDP glucose dehydrogenase (UGDH), with the majority of hyaluronan synthesis attributable to activities of HAS2 expressed by CD34− fibroblasts. Created with BioRender.com