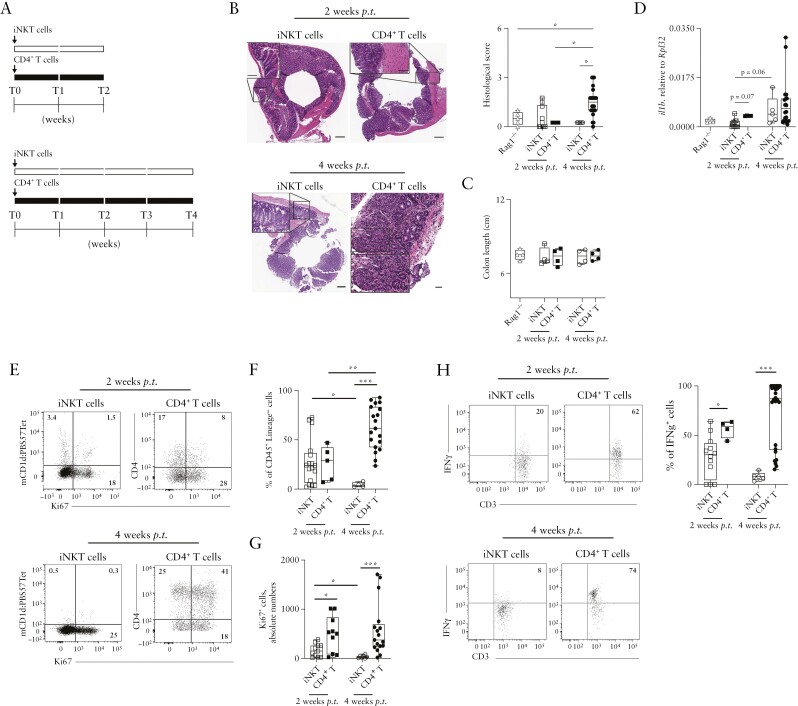
Figure 1.
iNKT cells are not pro-inflammatory when adoptively transferred in Rag1-/- hosts. [A] Schematic representation of the experiment. [B] H&E staining [left, scalebar 100 µm] and cumulative histological score [right plots] of colon specimens obtained at sacrifice 2 weeks [square symbols] or 4 weeks [round symbols] post iNKT [white symbols] or naïve CD4+ T [black symbols] transfer; Rag1-/- mice controls are also shown. [C] Colon length. [D] Il1β colonic expression at sacrifice 2- or 4-weeks post transfer. [E-G] Frequency of colonic iNKT cells and CD4+ T cells at sacrifice. Representative dot plots [E] for total [F] and Ki67+ [G] colonic iNKT cells [white symbols] and CD4+ T cells [black symbols] 2 or 4 weeks after transfer gated on CD45+ Lin- cells. [H] Representative dot plots and cumulative percentages of IFNγ-producing colonic iNKT cells and CD4+ T cells 2 or 4 weeks after adoptive transfer. Statistical significance was calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test corrected for multiple comparisons by controlling the false-discovery rate [FDR]; *p ≤0.05, **p ≤0.01, ***p ≤0.001. H&E, haematoxylin and eosin.