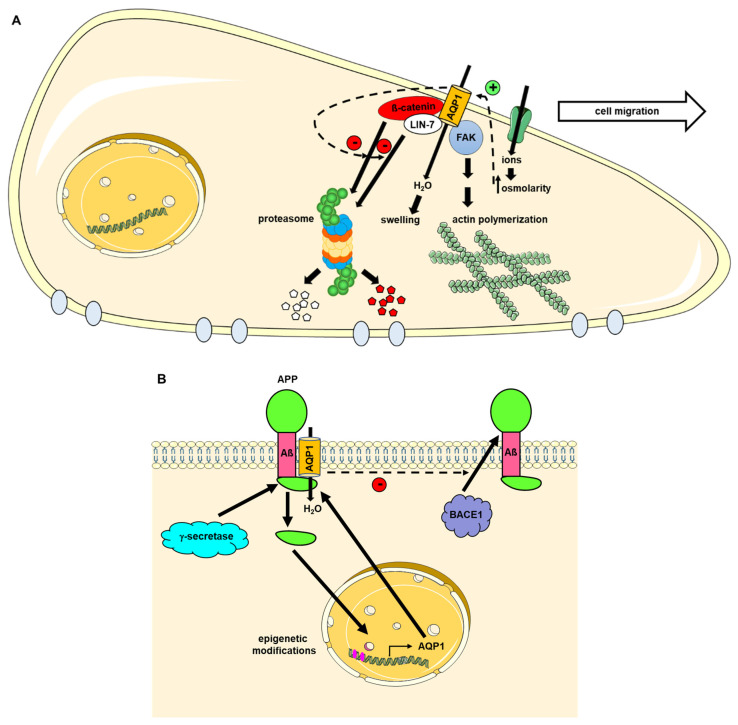
Figure 3.
Role of the protein–protein interactions involving AQP1. (A) Role in cell migration. During cell migration, increased ion transport at the leading edge of the cells raises intracellular osmolarity that subsequently drives water entry through AQP1. AQP1 binding to FAK, LIN-7 and ß-catenin promotes actin polymerization, at least partly by inhibiting LIN-7 and ß-catenin degradation through the proteasome. (B) Role in APP accumulation in Alzheimer’s disease. AQP1 interaction with APP reduces the binding of BACE1 to APP and inhibits the release of Aß. In addition, the N-terminus of APP released by γ-secretase induces epigenetic modification, leading to increased AQP1 expression. Aß: amyloid-ß peptide; APP: amyloid precursor protein; BACE1: ß-secretase; FAK: Focal-adhesion kinase; LIN-7: protein LIN-7 homolog.