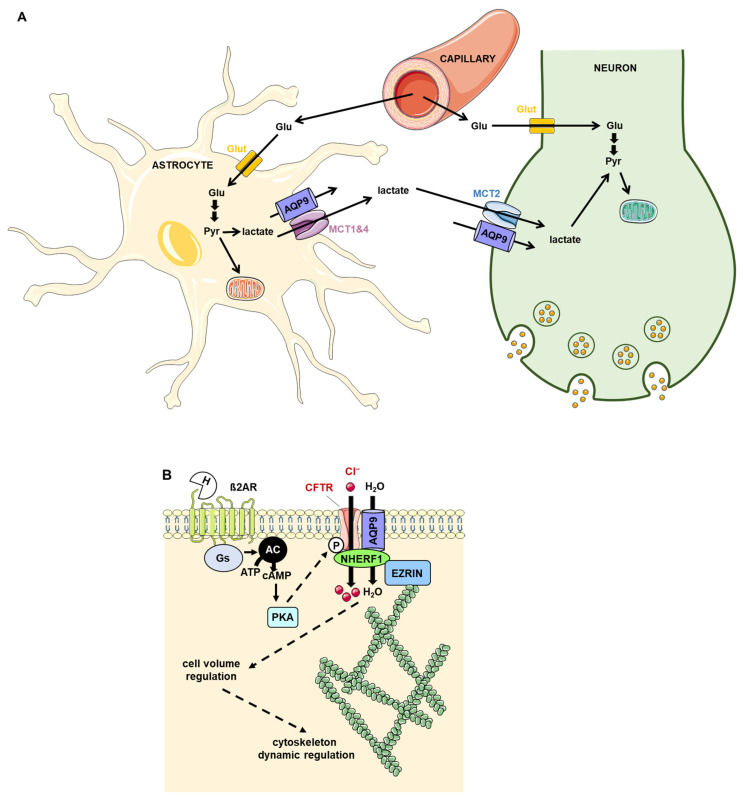
Figure 8.
Role of the protein–protein interaction involving AQP9. (A) Role in the astrocyte-to-neuron lactate shuttle. Glu enters astrocytes and neurons via GLUT and is transformed into Pyr. In astrocytes, Pyr either used by the mitochondria to produce ATP or is converted to lactate which exits the astrocytes through MCTs 1 and 4. Then, lactate enters neurons via MCT2 and is converted into Pyr, which is used to produce ATP in the mitochondria. Lactate may also directly pass through AQP9. (B) Role in vas deferens cells. Upon adrenergic stimulation, ß2AR is activated and leads to subsequent PKA activation, which in turn phosphorylates CFTR. CTRF–AQP9, CTRF–NHERF1 and NHERF1–AQP9 are likely involved in cell volume control. In addition, the NHERF1–Ezrin interaction is likely coupling cell volume control to cytoskeleton dynamics. AC: adenylyl cyclase; ß2AR: ß2 adrenergic receptor; CFTR: cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator; Glu: glucose; GLUT: glucose transporter; Gs: protein Gs; H: hormone; MCT: monocarboxylate transporters; NHERF1: Na+/H+ Exchanger Regulatory Factor; PKA: protein kinase A; Pyr: pyruvate.