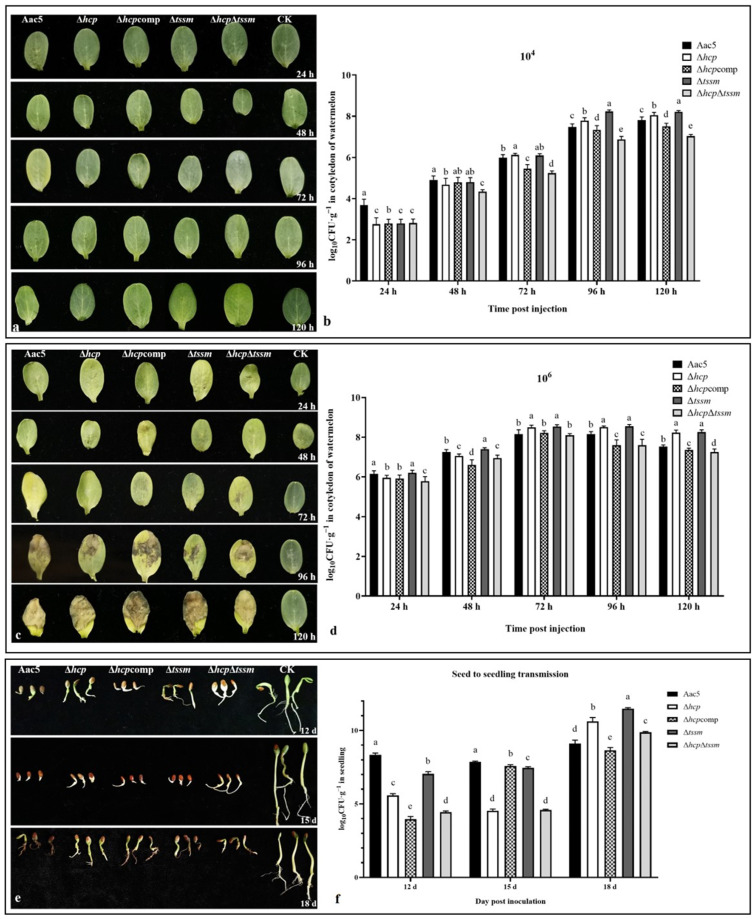
Figure 3.
Virulence and colonization of Acidovorax citrulli strains Aac5, Δhcp, Δhcpcomp, Δtssm, and ΔhcpΔtssm. (a) Symptoms caused by inoculation with WT, Δhcp, Δhcpcomp, Δtssm, ΔhcpΔtssm, and sterile water (CK) at 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 h post inoculation (hpi). The strains were cultured until the logarithmic phase, washed, resuspended in sterile water at 1 × 104 CFU·mL−1, and injected into the watermelon cotyledons. (b) Bacterial population levels in watermelon cotyledons. Significant differences were found between different letter substitutes on the column calculated by Duncan’s new multiple range test (p = 0.05). The strains were cultured until the logarithmic phase, resuspended in sterile water at 1 × 104 CFU·mL−1, and injected into the watermelon cotyledons. (c) Symptoms caused by WT, Δtssm, ΔhcpΔtssm, Δhcp, Δhcpcomp, and sterile water (CK). The strains were resuspended in sterile water at 1 × 106 CFU·mL−1 and injected into the watermelon cotyledons. (d) Bacterial population levels in watermelon cotyledons (1 × 106 CFU·mL−1). Significant differences were found between different letter substitutes on the column calculated by Duncan’s new multiple range test (p = 0.05). (e) Disease symptoms on germinating watermelon seeds at 12, 15, and 18 d. The strains were cultured to OD600 = 0.3 (3 × 108 CFU·mL−1), washed, and resuspended in sterile water. Seeds soaked in bacterial suspensions for 4 h were transferred to 15 mL centrifuge tubes containing sterile absorbent cotton, filter paper, and sterile water. (f) Bacterial population levels on germinating watermelon seedlings in the seed-to-seedling transmission assay. Significant differences were found between different letter substitutes on the column calculated by Duncan’s new multiple range test (p = 0.01).