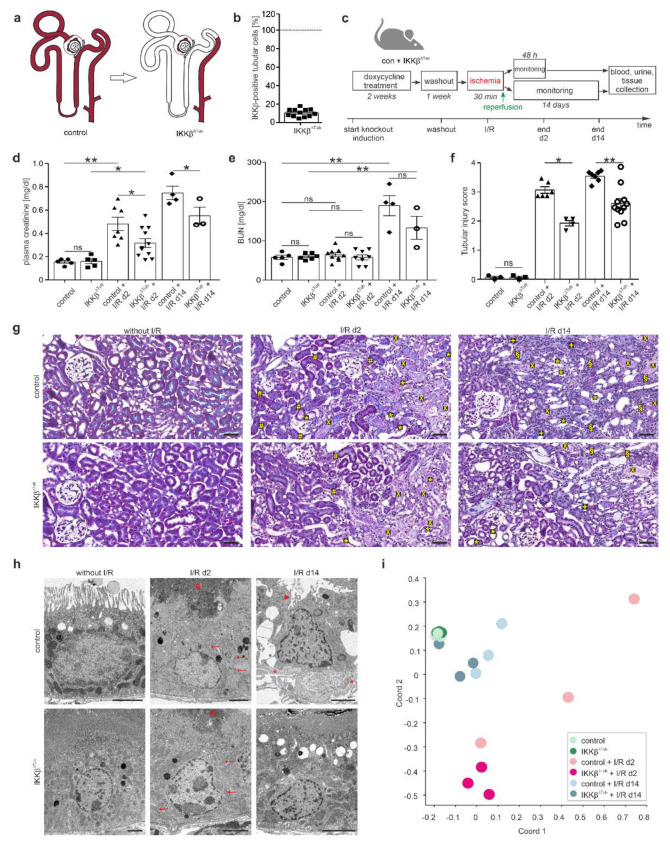
Figure 1.
Genetic tubular IKKβ-deletion ameliorates I/R injury. (a) Scheme illustrating deletion of IKKβ gene under Pax8 promoter along the tubule; (b) semi-quantitative analysis of IKKβ mRNA expression derived from Exon 3 in tubular cells of control and IKKβ∆Tub. Arithmetic means ± SEM of n = 12 per group; * p < 0.05, t-test; (c) timeline of experimental procedure; (d,e) plasma creatinine (d) and blood urea nitrogen (BUN; (e)) values of control and IKKβ∆Tub at baseline, 2 days and 14 days after I/R injury. Arithmetic means ± SEM of n = 3–11 per group; (f) semi-quantitative evaluation of tubulointerstitial injury. Arithmetic means ± SEM of n = 3–11 per group; (g) representative images of Masson trichrome stained kidney section of control and IKKβ∆Tub at baseline, 2 days and 14 days after I/R injury. Scale bar = 50 µm. Tubular necrosis (x), loss of brush border (*), eosinophilic debris (#) and cellular infiltration (§) and fibrotic areas (+) are shown; (h) representative electron microscopy images of control and IKKβ∆Tub at baseline, 2 days and 14 days after I/R injury. Scale bar = 2 µm. Reduced visibility of mitochondria (arrow), cellular debris (#), loss of brush border (arrow head) and basement membrane thickening (*) are encountered; (i) principal coordinate analyses between control and IKKβ∆Tub at baseline, 2 days and 14 days after I/R injury displayed as variation between samples; IKKβ∆Tub vs. control at baseline, at 2 days and 14 days after I/R injury based on filter criteria DESeq p-values < 0.05; fold change > 1.5. For (d–f) * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, Mann–Whitney–U test (if n < 4 Lord test).