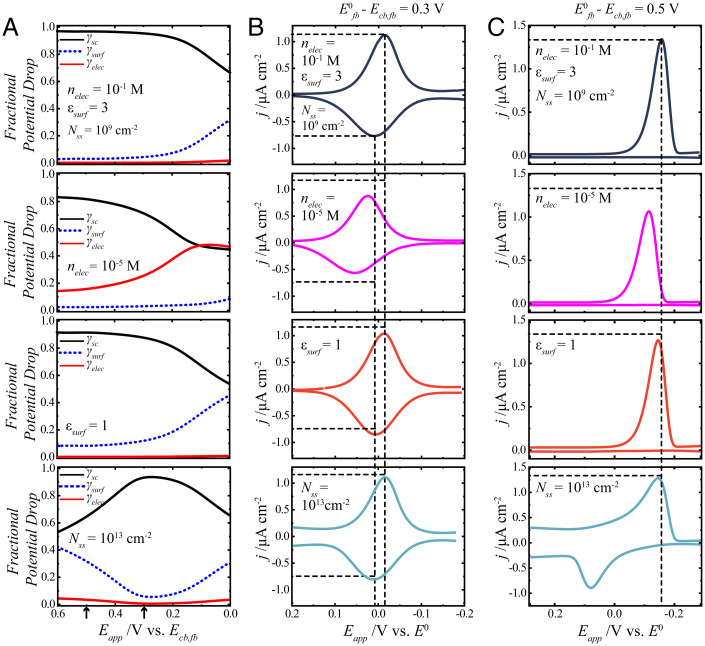
Fig. 3.
Summary of the effect of changing selected physical parameters (nelec, εsurf, and Nss) that define a redox adsorbate on a lightly doped n-type semiconductor electrode without coupling. The full list of calculation values is contained in SI Appendix, Table S1. (A) The fractional potential drops are represented as γsc (black solid lines), γsurf (blue dashed lines), and γelec (red solid lines) as a function of potential. The potential scale is referenced to the conduction band–edge value at the flat band, Ecb,fb. The arrows on the x axis denote the zero point of the voltammograms in C and B, respectively. (B) Calculated j-Eapp responses for a redox adsorbate with a standard potential that is +0.3 V relative to Ecb,fb. These plots use the specific γsc, γelec, and γsurf values from A and B in Eqs. 1, 23, and 31 and assume a scan rate of 0.1 V s−1. (C) Calculated j-Eapp responses for a redox adsorbate with a standard potential that is +0.5 V relative to Ecb,fb. The top row represents a reference condition with the relevant parameter values listed on the plots. The subsequent rows indicate the effect of changing one parameter to the value indicated on each plot.