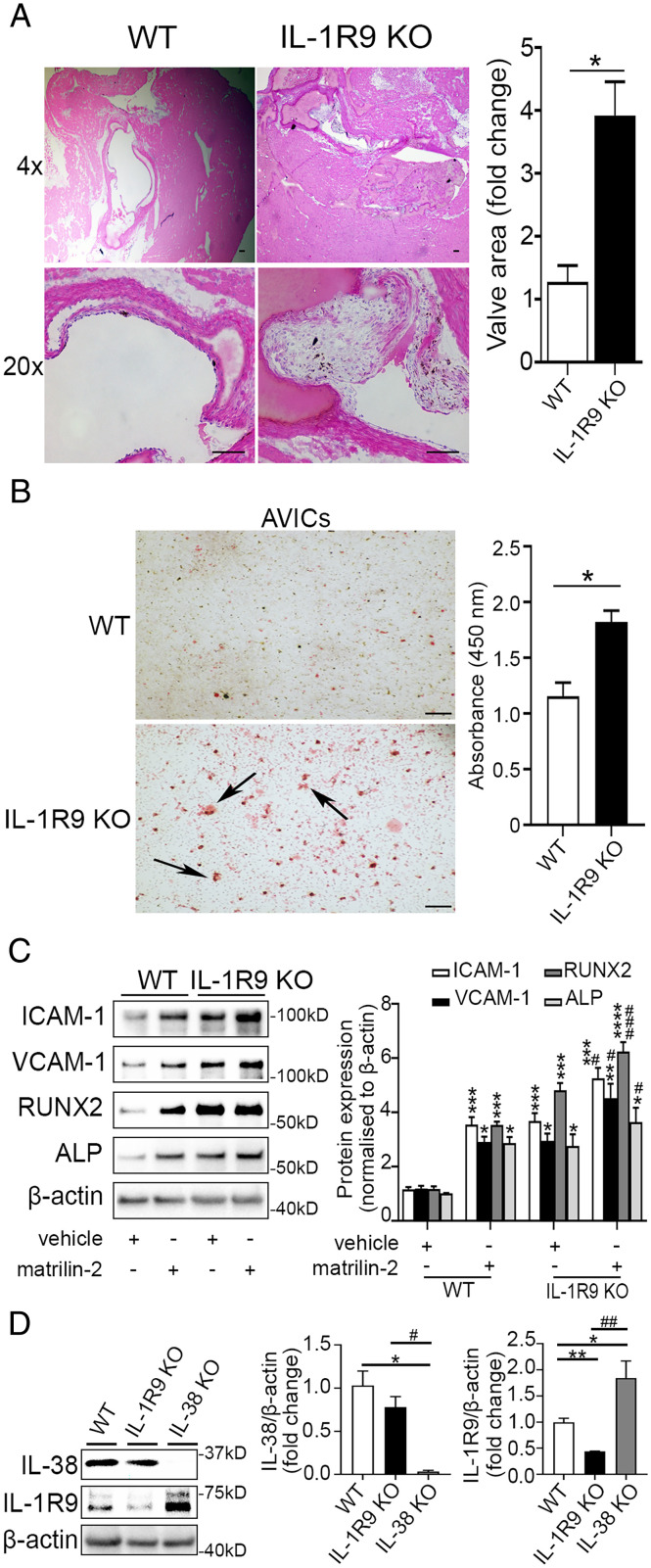
Fig. 4.
Effects of IL-1R9 deficiency on aortic valve. (A) Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin staining of aortic valves show that valve leaflet thickening was occurred in IL-1R9 KO mice (12 wk old) in the absence of any treatment. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 3 mice per group. *P < 0.05 versus WT. (Scale bar, 100 µm). (B) Representative images of Alizarin Red S staining (Left) and spectrophotometric data (Right) show that mouse AVICs from IL-1R9 KO mice displayed greater calcium deposition compared to mouse AVICs from WT mice. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 3 mice per group. *P < 0.05 versus WT. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C) Mouse AVICs from WT and IL-1R9 KO mice were treated with vehicle or matrilin-2 (2 µg/mL) for 72 h. Representative immunoblots (Left) and densitometric data (Right) show that mouse AVICs from IL-1R9 KO mice had greater inflammatory and osteogenic responses to matrilin-2 stimulation. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 4 mice per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001 versus WT vehicle; #P < 0.05 and ###P < 0.001 versus WT + matrilin-2. (D) Representative immunoblots (Left) and densitometric data (Right) show that IL-1R9 protein levels were slightly increased in mouse AVICs from IL-38 KO mice than those from WT mice, and IL-38 protein levels in mouse AVICs from IL-1R9 KO mice were similar to those from WT mice. Values are mean ± SEM, n = 3 mice per group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus WT; #P < 0.05 and ##P < 0.01 for IL-38 KO versus IL-1R9 KO.