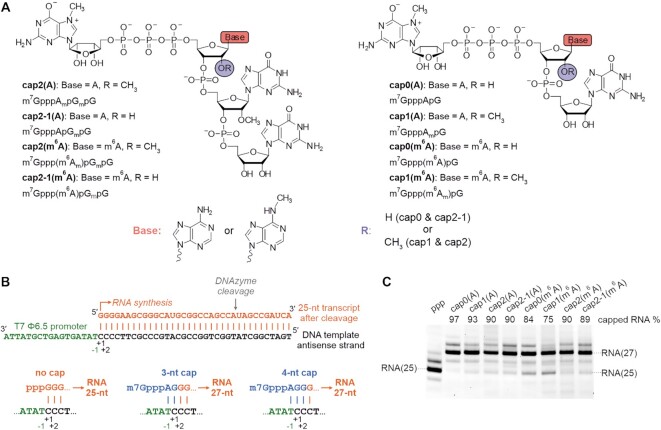
Figure 1.
Tetranucleotide cap analogues act as initiators of in vitro transcription reactions. (A) Structure of the cap analogues used in this study; newly synthesized tetranucleotide and previously obtained trinucleotide (14) cap analogues are presented on the left and right side, respectively. (B) Comparison of the major transcription initiation events during the in vitro transcription reaction when either no cap analogue, a trinucleotide cap analogue or a tetranucleotide cap analogue was used as an initiator. Capped RNA obtained in the in vitro transcription reaction with a tri- or tetranucleotide cap analogue is 27 nt long, as uncapped RNA is 25 nt long. (C) Analysis of short RNAs obtained by in vitro transcription using T7 RNA polymerase in the presence of different cap analogues (DNAzyme-trimmed and HPLC-purified transcripts). The capping efficiency values (percentage) determined by densitometric quantification of the major bands corresponding to capped and uncapped RNA are shown at the top of the gel. Minor extra bands most probably arise from unspecific addition of nucleotides during in vitro transcription.