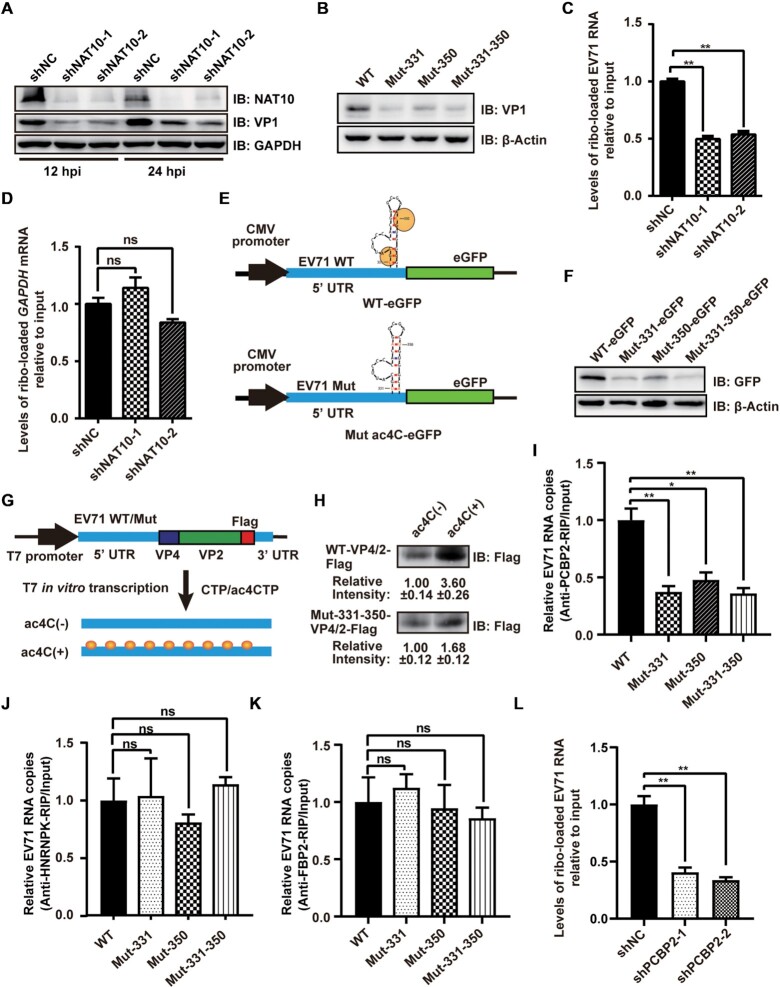
Figure 3.
ac4C enhanced the translation efficiency of EV71 RNA. (A, B) Western blot analysis of extracts of NAT10-knockdown RD cells infected with EV71 at 12 and 24 hpi (A) or Vero cells infected with EV71 WT and ac4C mutants at 24 hpi (B). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (C, D) Vero cells with or without NAT10 knockdown were infected with EV71 and used to analyze input and ribosome-loaded RNA levels for EV71 (C) and GAPDH (D) at 24 hpi. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). **P ≤ 0.01, ns: not significant, unpaired Student's t-tests. (E) Schematic representation of the eGFP reporter vector with insertion of the 5′ UTR of EV71 WT or ac4C mutants. (F) Representative western blots of extracts from RD cells transfected with eGFP reporter vectors (E) at the indicated times post-transfection. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (G) Schematic representation of the in vitro translation template. Yellow solid circles indicate ac4C modification. (H) In vitro translation assays were performed using ac4C(±) RNA template. Gray intensity was quantified using ImageJ. Data are means ± SDs (n = 3). (I–K) Binding of PCBP2, HNRNPK, and FBP2 to RNA from EV71 WT or ac4C mutants. EV71 WT- or ac4C mutant-infected Vero cells were crosslinked with formaldehyde and subjected to IP using anti-PCBP2 (I), anti-HNRNPK (J), or anti-FBP2 (K) antibodies. Expression was quantified using qRT-PCR. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ns: not significant, unpaired Student's t-tests. (L) shNC- or shPCBP2-treated Vero cells were infected with EV71 and used to analyze input RNA and ribosome-loaded RNA levels of EV71 at 24 hpi. Data are means ± SEMs (n = 3). **P ≤ 0.01, unpaired Student's t-tests.